
Chapter 1
Before we dive into specific techniques and aspects of how to learn SEO in 2020, let’s start with the basic stuff in the first chapter. Are you ready? Welcome to the ultimate SEO guide for beginners!
Are you new to SEO? Do you wonder how it works and what matters most in 2020? You’re at the right place!
What is SEO?
Search engine optimization (SEO) is a process of improving positions in organic (non-paid) search results in search engines. The higher the website is, the more people see it.
The history of SEO dates back to the 90s when the search engines emerged for the first time. Nowadays, it is an essential marketing strategy and an ever-growing industry.
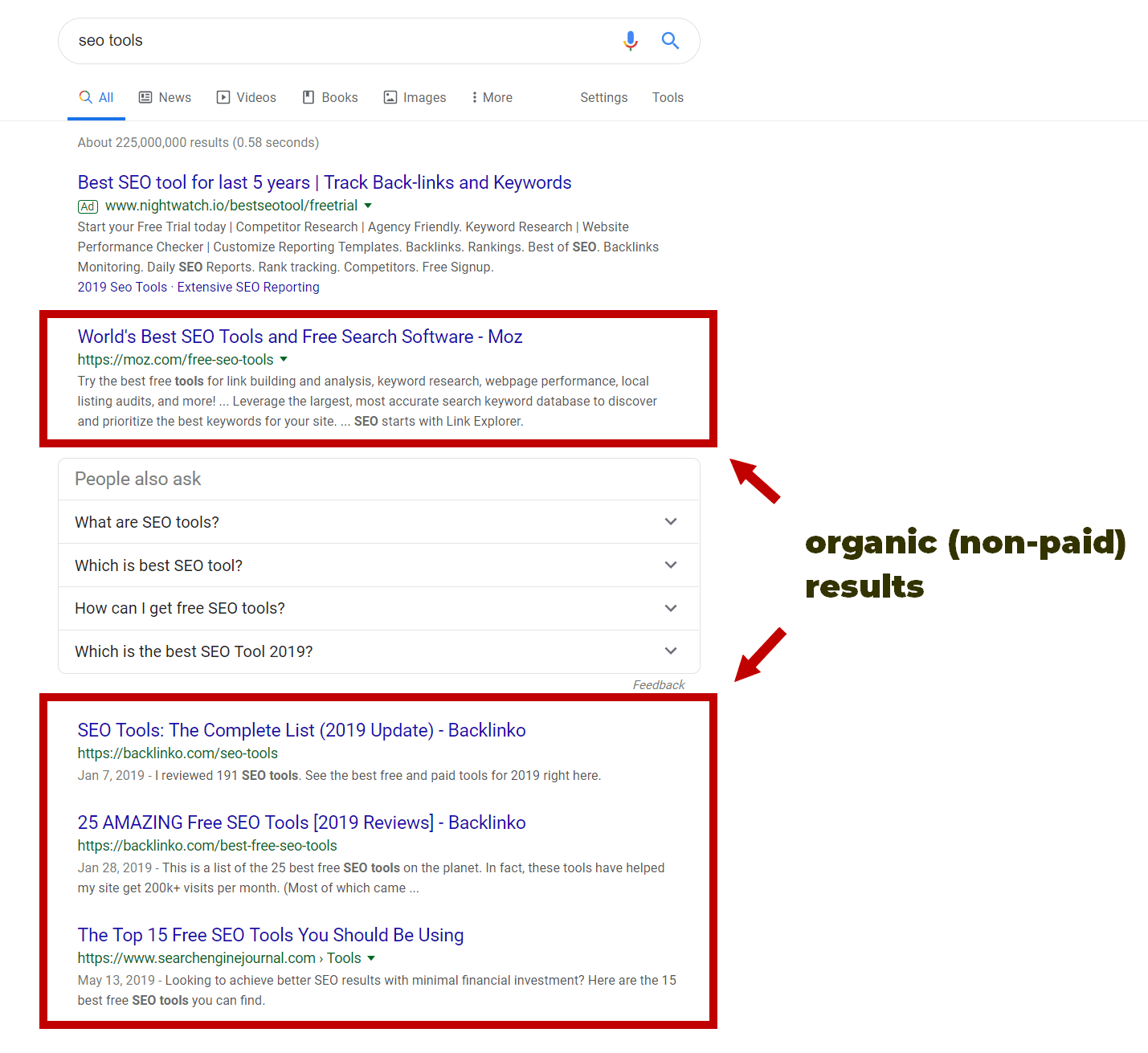
If you want to learn SEO, you should be ready for a lot of creative, technical and analytical work. There are many techniques with different goals, however, the main point will remain the same – to be among the highest results in organic searches.
Simply said, SEO is about running the right website for the right people.
It isn’t only about a perfect structure or technical background of the website. Your website has to be filled with quality and well-optimized content tailored to the needs of your audience. And of course, it has to be good enough to be linked from other websites.
Is SEO difficult?
Search engines such as Google, Bing, Yahoo! and others index websites to create an order based on various ranking algorithms. Can we identify these algorithms? Yes and no.
Google uses more than 200 ranking factors. Though we know many of them: quality content, backlinks, or technical things such as site speed, there are many of them kept as a secret.
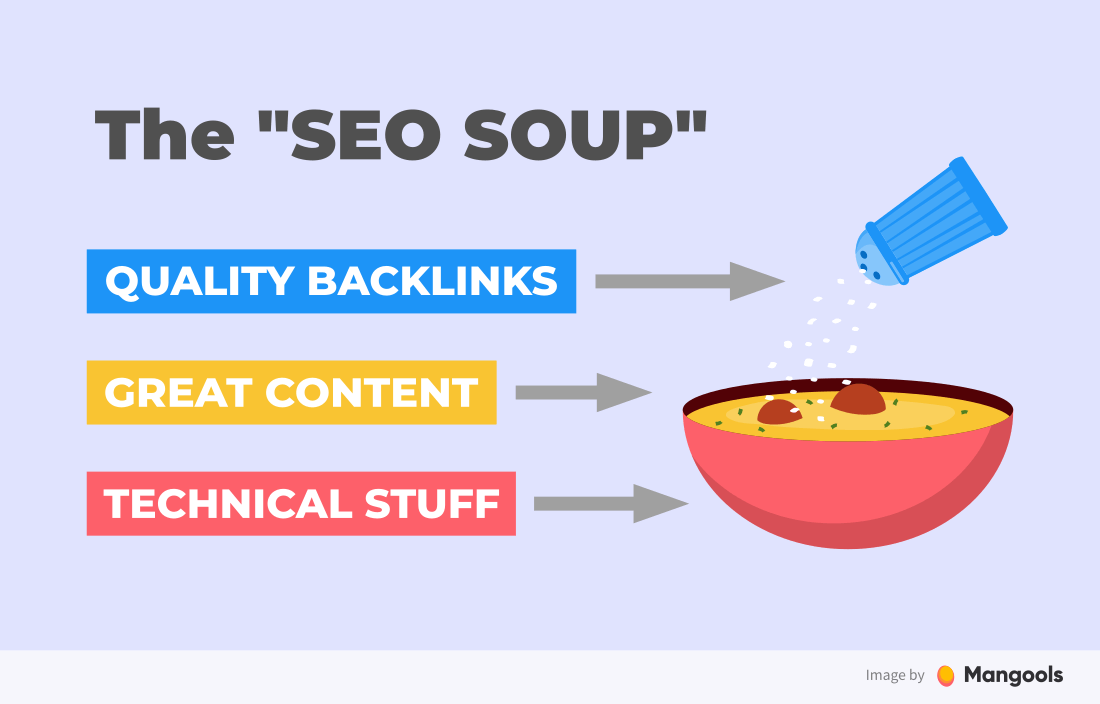
Of course, you don’t need to know all the factors to rank with your website. To understand what SEO is all about, imagine a bowl of soup. There are three important aspects:
- The bowl represents the technical stuff behind the website (technical and on-page SEO) – without proper bowl, the soup would spill all over the table.
- The soup represents the content of your website – it is the most important part. Bad content = no rankings, it is that simple.
- The seasoning represents the quality backlinks increasing the authority of your website – the last ingredient to make your SEO soup perfect.
The search engines are used by internet users when they are searching for something. And you want to be that “something”. It doesn’t matter whether you sell a product, service, write a blog, or anything else, search engine optimization is a must.
Your website needs to be indexed by search engines. Otherwise, you’re lost.
Wise SEO techniques improve your rankings in the search engine results page (SERP). Higher rankings mean higher traffic. If the traffic is engaged, it will bring conversions.
To sum it up, if you plan to succeed with your website, you need to do SEO. Some aspects are more complicated, but very often, the SEO success stands on common sense and a few best practices.
How can I learn SEO? Do I need someone’s help?
Even the basic changes can make a huge difference in how search engines see your website. In this ultimate SEO guide for beginners, we’ll cover all the critical topics and SEO basics. You’ll gain enough knowledge to proceed with SEO on your own.
If you wonder how to learn SEO in 2020, we have a simple answer for you: You’ll need a lot of study and practice. The good thing is that you’ll find tons of information on the internet for free (including this SEO guide) but you should choose wisely. On top of that, you can attend various courses, classes or webinars.
If you don’t want to bother yourself that much or don’t have time, you can ask SEO consultants, specialists or agencies for help. Keep in mind that this way won’t be for free compared to this guide.
Basic terms vocabulary
- On-page vs. off-page SEO
- White hat vs. black hat vs. grey hat SEO
On-page vs. off-page SEO
Doing On-page (on-site) SEO means optimizing your website to affect the organic search results. It’s everything you can do on the website – from content optimization through technical aspects:
- meta tags
- headings
- URL structure
- image SEO
- content
- structured data
- website size and speed
… and many others. We deal with them in the 3rd chapter.
Off-page (off-site) SEO covers all activities you can do to improve the website SEO authority through getting backlinks from other websites. There are many ways to get them:
- email outreach
- guest blogging
- submissions
- social media efforts
- cooperation with influencers
- writing valuable content, so people would love to link to your website
… and many others that are covered in the 6th chapter.
White hat vs. black hat vs. grey hat SEO
Black hats vs. white hats have their origin in Western movies. It’s like bad guys vs. good guys. But don’t take these words too seriously. Opinions on both SEO approaches tend to differ.
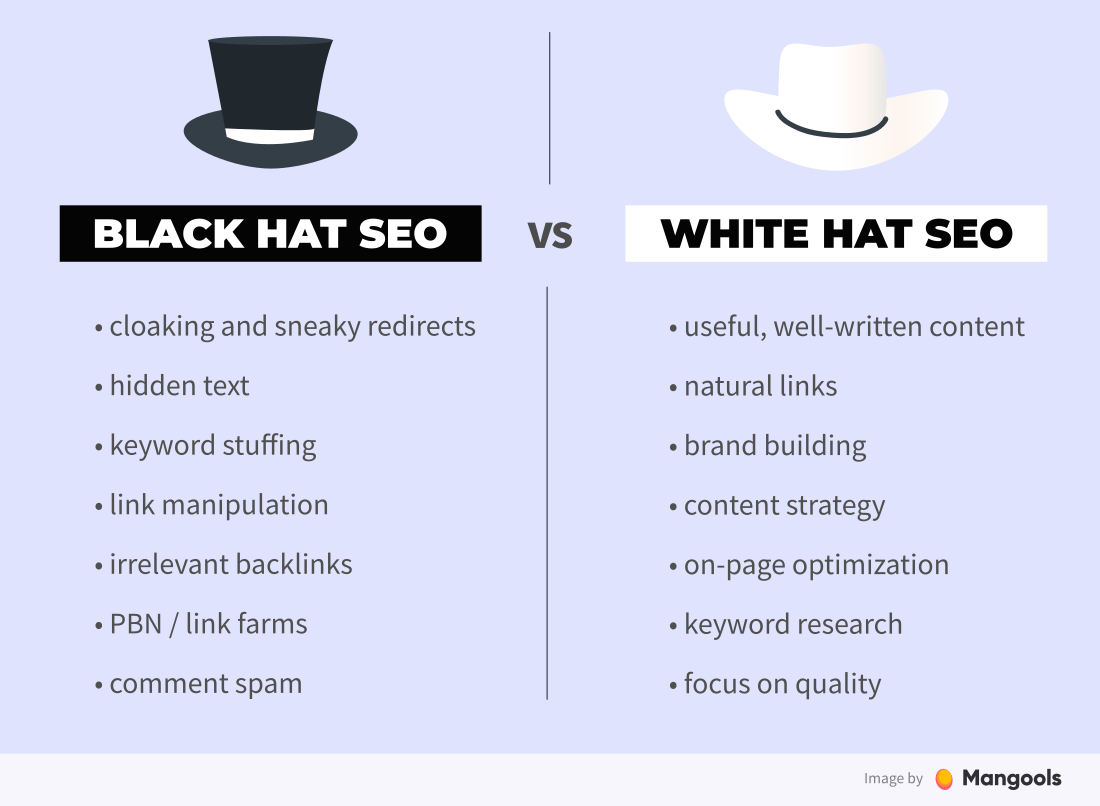
Black hat SEO is a set of unethical practices to improve rankings of a website in the search engine results page. They are designed to affect search engines while not taking human factor into consideration.
Black hat SEO can get you to the top of the SERP in a short time, however, search engines will most probably penalize and ban the website sooner or later.
Lists of violating practices can be found in Google’s Webmaster Guidelines or Bing’s Webmaster Guidelines.
White hat SEO is a set of ethical techniques sticking to the guidelines and rules. The basic parts of white hat SEO are:
- quality and relevant content
- overall website optimization
- link building
White hat SEO is a long-term strategy oriented to improve the user experience. Generally speaking, being a good guy in the world of SEO is considered the proper direction.
There’s also a term called the Grey hat SEO, a practice when you may risk less when compared to the Black hat techniques. Grey hat techniques aren’t clearly defined by Google so you can gain thousands of website users while not being penalized or lost all your rankings a day after.
Generally speaking, you don’t want to make Google your enemy.
Chapter 2
In the 2nd chapter of this SEO guide, you will learn how search engines work, how people use them and what type of search queries they submit. We’ll take a look at the technical background behind Google.
Let’s take a closer look at the search engines and what are the most typical ranking factors you should focus on.
How search engines work
Search engines consist of three main ingredients:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Picking the results
The process goes like this:
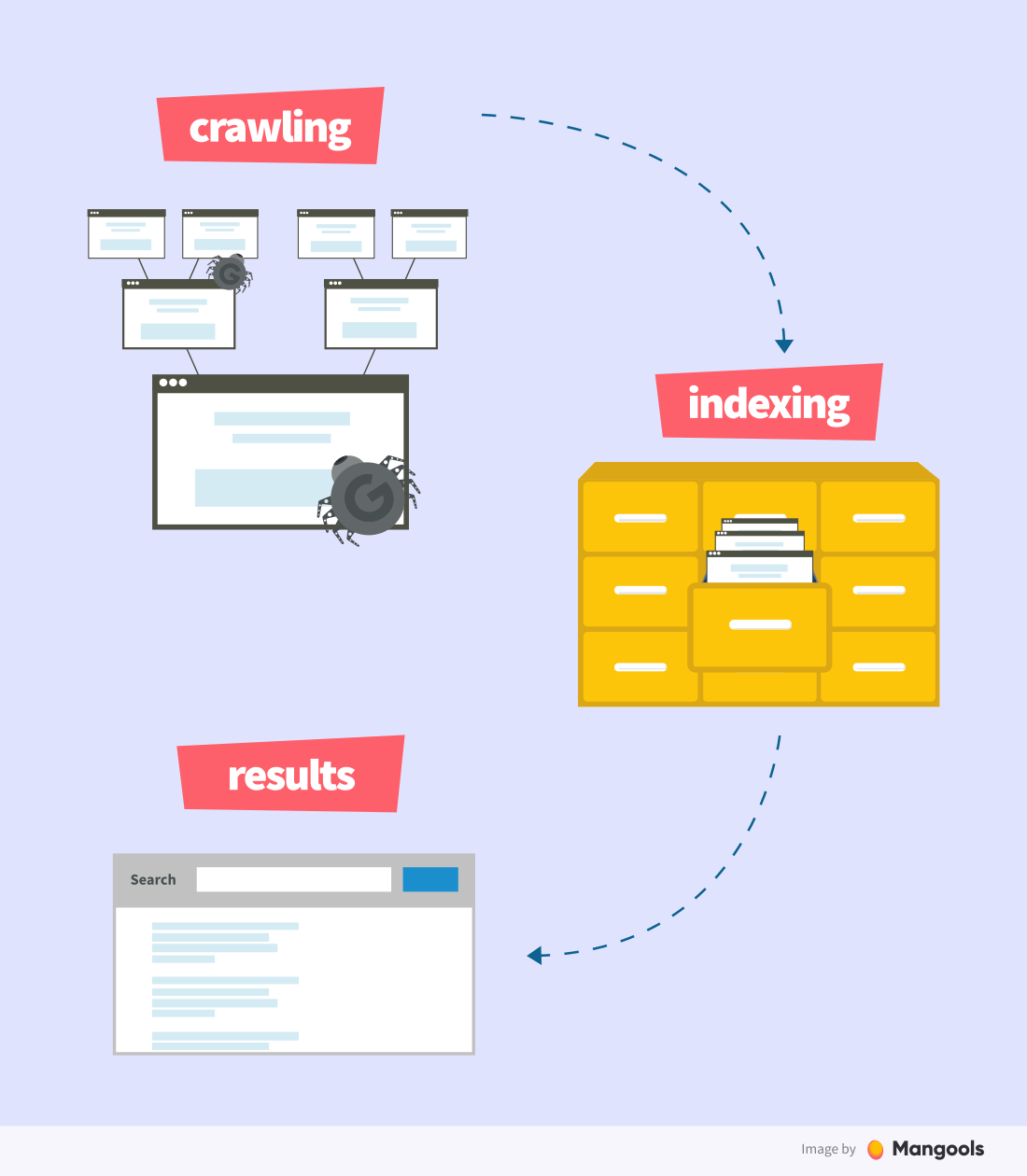
Crawling
Crawling or spidering means scanning the website, its sections, content, keywords, headings, hyperlinks, images by thousands of small bots. Any data that can be found on the website is crawled.
Crawlers detect all hypertext links on a website that point to other websites. Then they parse those pages for new links over and over again. Bots crawl the whole internet regularly to update the data.
Indexing
Once the website is crawled, the indexing takes place. Imagine the index as a gigantic catalog or a library full of websites from all over the world. It usually takes some time for a website to be indexed. From our experience, it’s from 1 to 10 days.
Furthermore, every time it’s changed, our good friend crawler scans it again. Keep in mind that until the updates on the website are indexed, they won’t be visible in search engines.
Picking the results
Results are critical for both developers and users. Once the internet user submits a search query, the search engine digs into the index and pulls out matching results. It’s a process of checking the query against billions of websites based on various algorithms.
Companies running search engines (Google, Microsoft, Yahoo!) keep the exact calculations of their algorithms in secret. Nonetheless, many ranking factors are well-known.
Ranking factors
Most of these factors are proven, but some are just speculations or even myths. On top of that, some are more important than others. Cyrus Sheppard from Zyppy made a nice list of Google ranking factors.
You don’t have to know all of the ranking factors by heart to learn SEO, but it is good to have at least a basic overview.
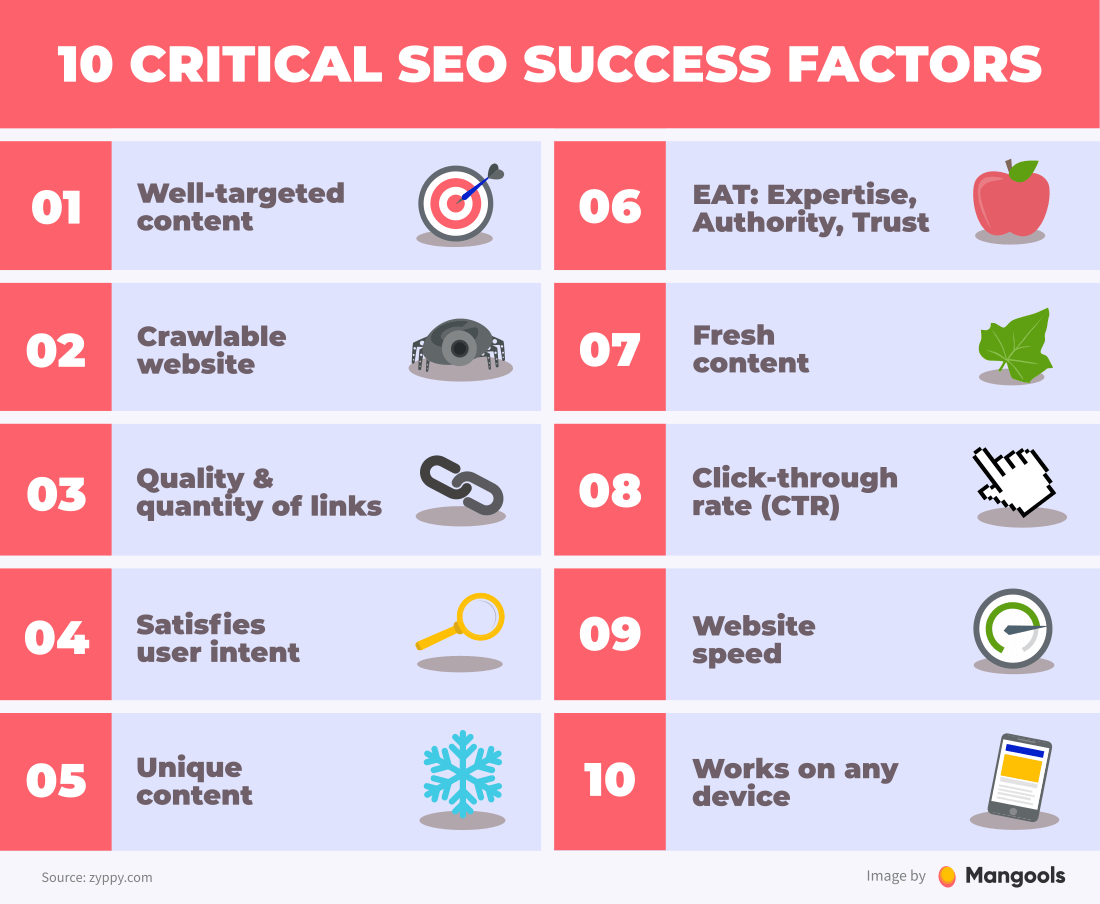
One of the most important factors, the backlink profile is based on the number and quality of backlinks leading to a website. It’s a very simplified view on Google approximation of the website’s authority. Each backlink is basically an analogy of an academic citation.
Some other important ranking factors include (in no particular order):
- use of relevant keywords and phrases
- HTTPS
- link relevance
- grammar and spelling
- topical authority
- social sharing
- domain age
- AMP
- page layout
Ranking factors can be divided into on-page SEO factors (including technical SEO) and link building or off-page SEO factors.
How people use search engines
To recap: The main point of SEO is to be friendly both to users and search engines. If you invest all your money and time into perfect technical SEO, it’s fine. But if the user interaction is poor, your positions can suffer. And that’s how you start wasting money. The user’s point of view is a number one priority.
The picture below represents one of the common user journeys in Google Search:
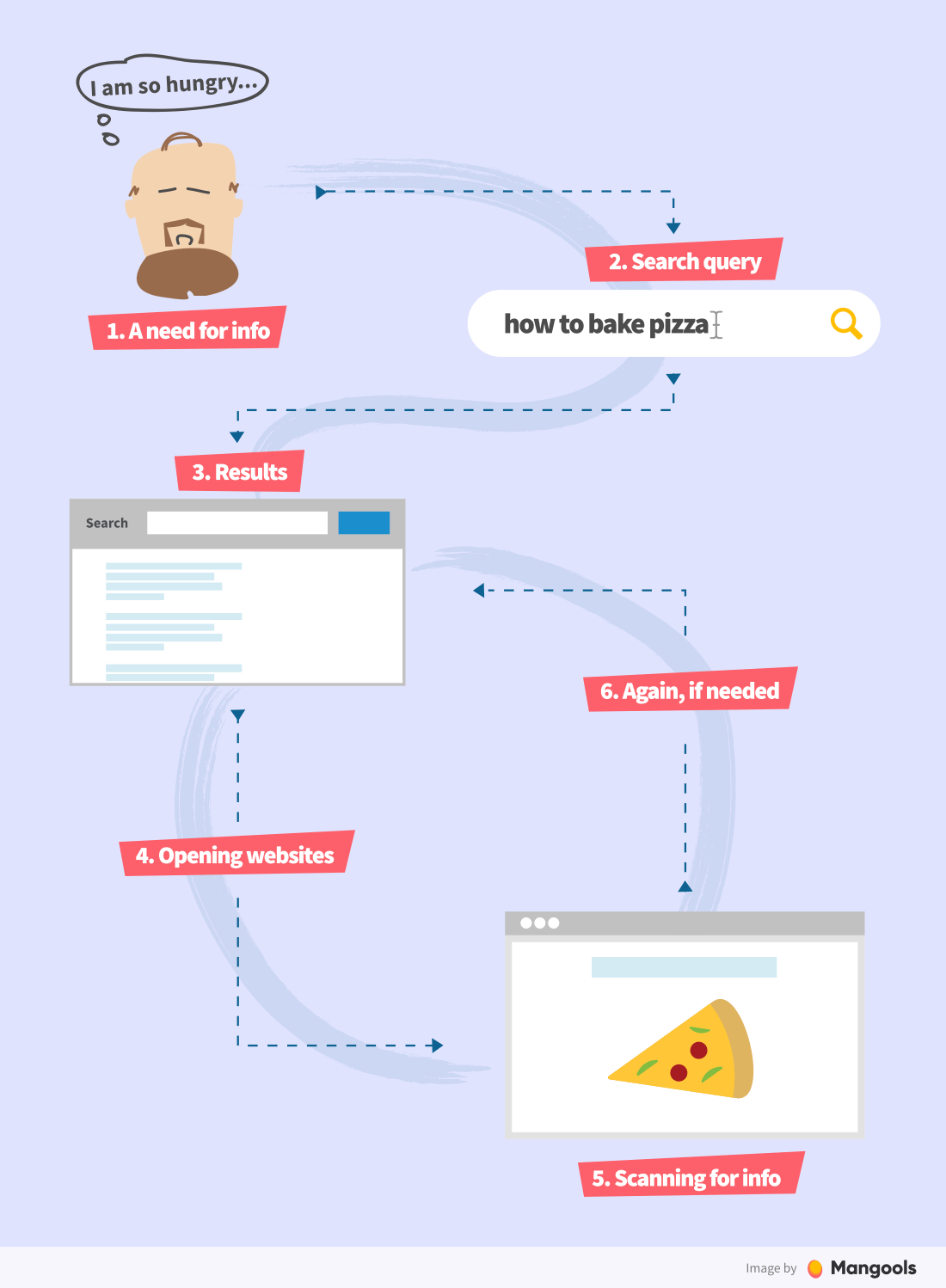
The interactions with search engines have evolved over the years. However, the principle remains the same:
- A need for a solution, information, or an answer
- Typing the need in form of a query (keyword) into the search engine
- Going through the first results
- Clicking on one or more results (websites)
- Scanning websites for the answer
- Going through more results on the 1st SERP and/or changing the search query, if the answer isn’t found.
Search engines market share
In the charts below, you can see which search engines people use the most. The data is from Netmarketshare’s reports.
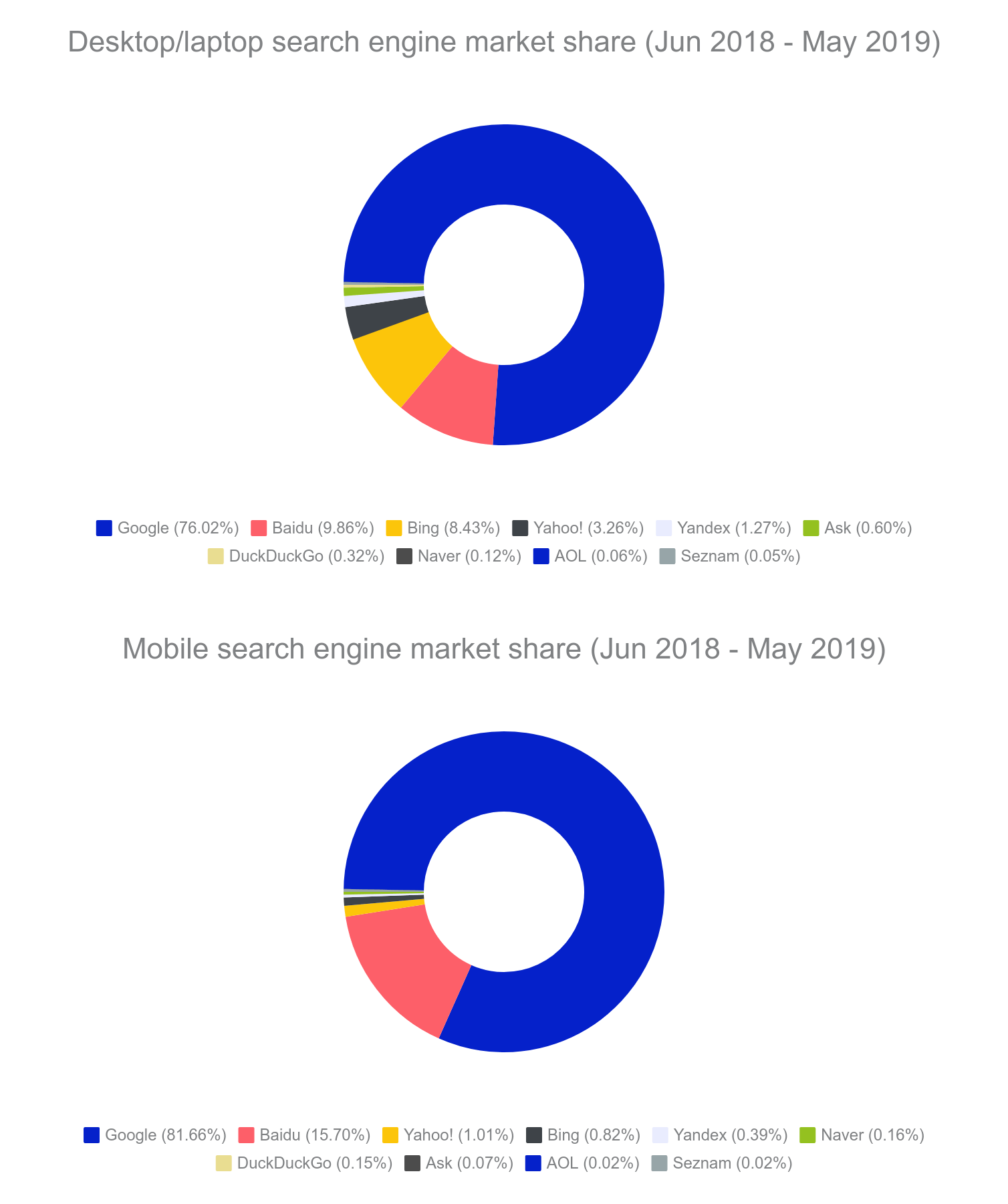
Find out more about the most popular search engines and their history.
How do we classify search queries?
There are three types of search queries:
- Navigational search queries
- Informational search queries
- Transactional search queries
Navigational search queries
They represent an intent to search for a particular brand or website. People tend to type “youtube” or “google” into search engines rather than using browser’s history or bookmarks.
Based on our case study where we analyzed 1,6 billion keywords, brands such as YouTube, Facebook and Google reach the highest search volumes along with other navigational search queries.
Informational search queries
These are submitted when users are searching for information. They aren’t looking for a particular website, yet for an answer or guidance on how to do something. For example, “How to bake pizza”.
Transactional search queries
This type is an intention to make a transaction. It usually comes with a product name (Nike Airmax) or category (sneakers). Additionally, it can be written with “Where to buy …”, “… price” or in a similar manner.
There are many blog posts on how to target a particular search query. However, it’s may not be that easy in the future because of the increasing popularity of voice assistants such as Siri, Google Now or Alexa.
Informational search queries can quickly transform to transactional by opening a new app or giving an option to make a purchase.
SERP updates
Being on the first page of the organic search results is good, scoring the top three is great but there’s only one winner, right? Or, is it? It’s a matter of perspective.
Websites all over the world are updated on a daily, weekly or monthly basis, …ok, some are not but that’s a different case. The thing is that the internet grows every single day. When new websites and changes are indexed by a search engine, the organic results may change.
Another very important factor is Google algorithm which changes all the time. Minor tweaks may not cause anything at all, but a major algorithm update can end up as an earthquake.
What we’re trying to say is that even if you’re the winner, your positions can (and probably will) be replaced by competitors the other day, and vice versa.
In the chart below, you can see the importance of the highest rankings in Google depending on their organic click-through rate (CTR) distribution for May 2019 (based on data by Advanced Web Ranking).
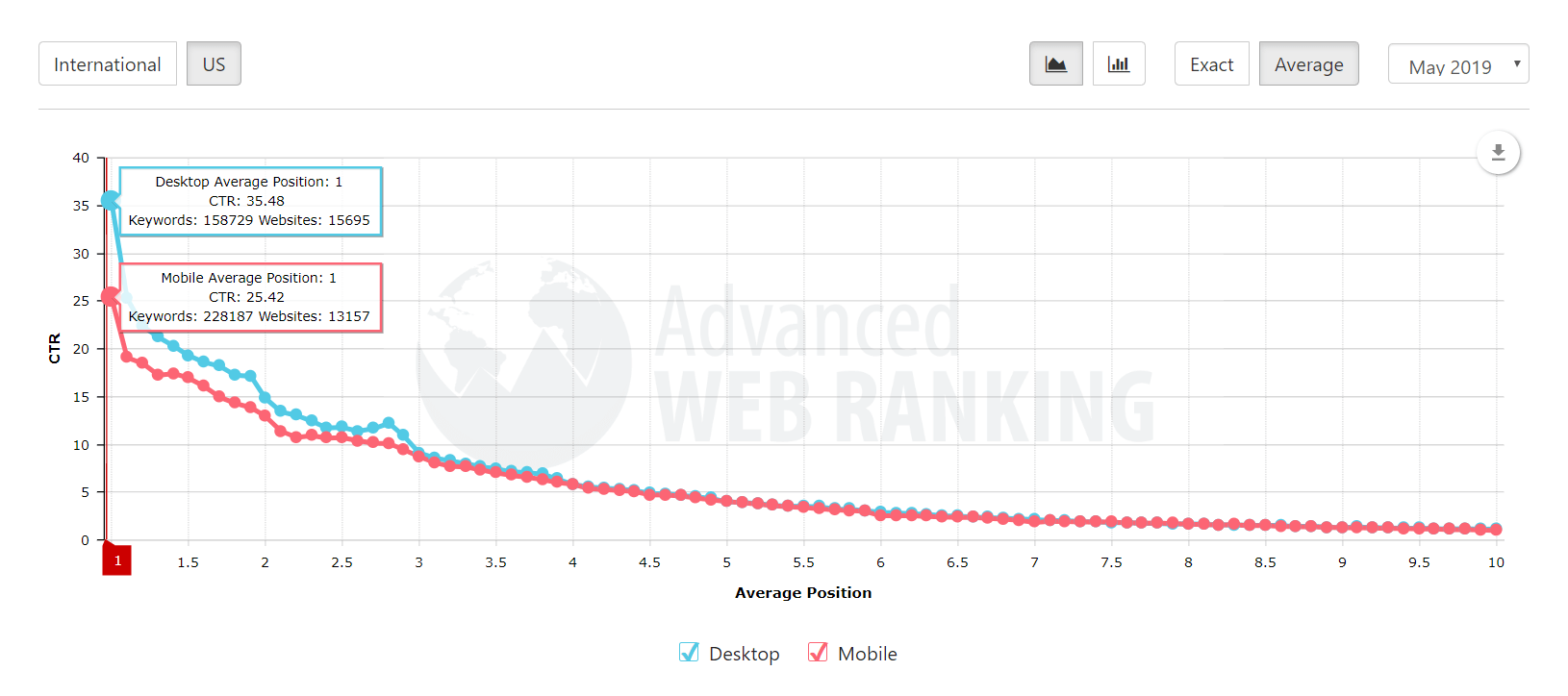
SERP features
Of course, ranking first is important, but these days, you have to take into consideration the so-called “zero position”.
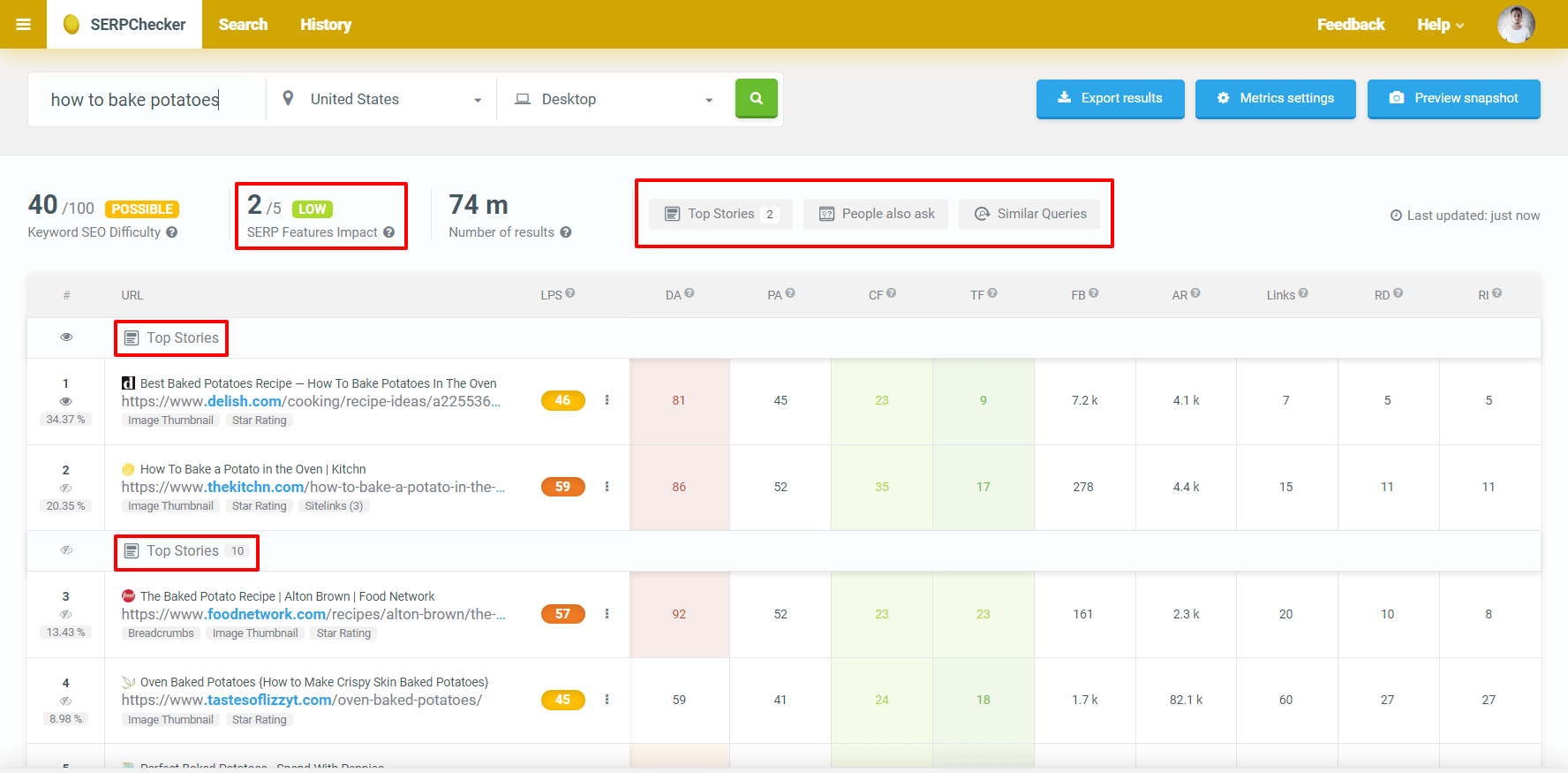
Let’s take a look at the results for “How to bake potatoes” search query. The first result is a Google featured snippet with all or the most important information, so you don’t need to check the other results.
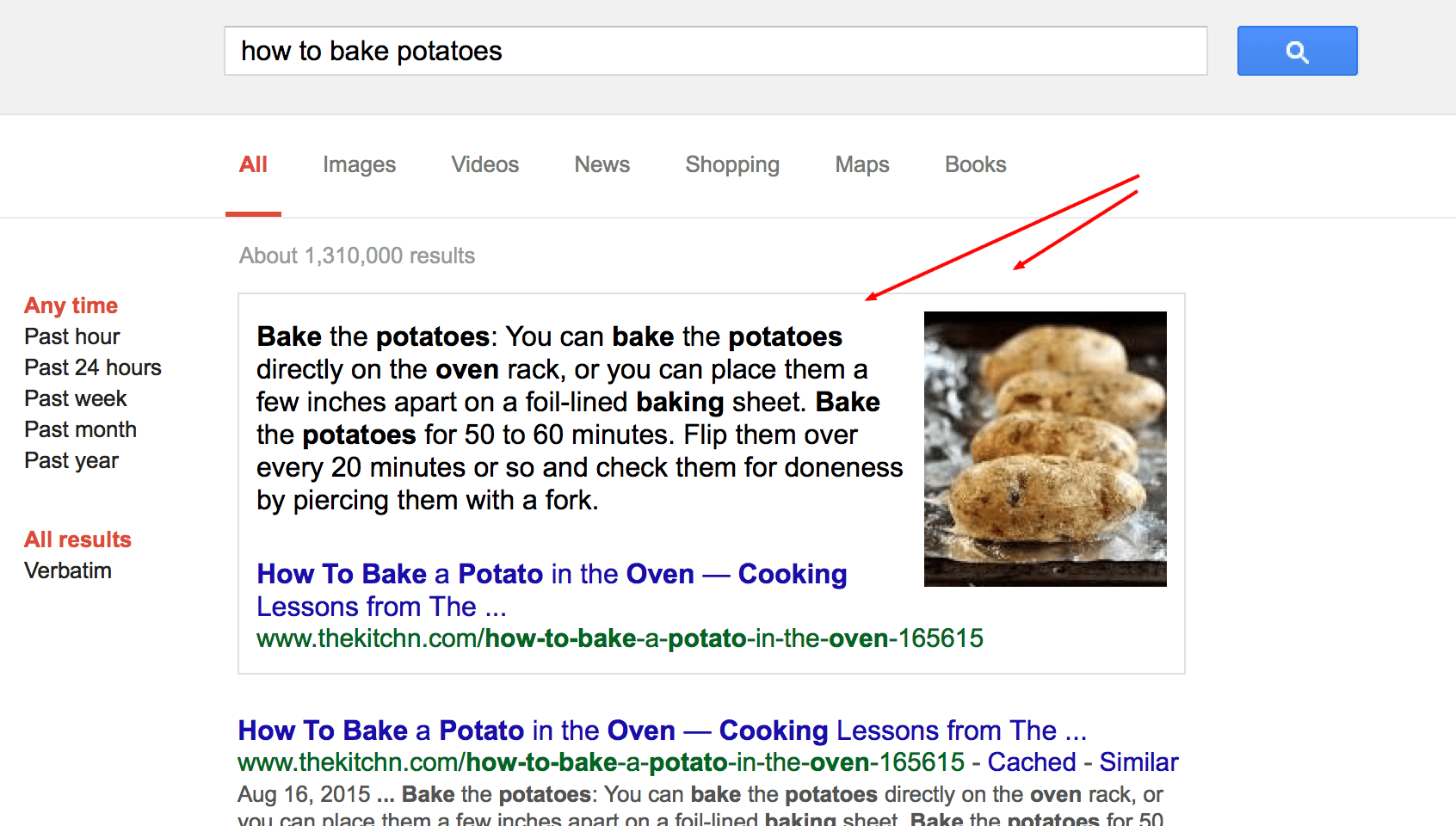
There are many SERP features (also called Rich snippets). Why should you care about them? Rich snippets influence the behavior of users when they see the SERP. In other words, the generic organic search results may have and in many cases, they do have lower click-through rates (CTR).
It’s because the SERP features have bigger visual appeal and they often provide enough information so the Google Search users don’t have to click on other results at all or they click only on the featured results.
These are some of the most common rich snippets you’ll see in the SERP:
- Featured snippet
- Answer box
- Carousel (images, videos, products)
- Image pack
- Map pack
- Sponsored features (Google Ads, flights, shop on Google)
- Knowledge graph
- Top stories
- Events
- Sitelinks
The good thing is that there are ways to spot and analyze the impact of these enhanced results. For example, SERPChecker will do the job.
Just type in the keyword, select the location and device type. This tool will show you the search results and SERP features if there are any. It estimates the impact on a scale from 0 to 5.
To find out more, click on the feature. You can also see the actual appearance of the SERP if you click on the “Preview snapshot”.
Chapter 3
On-page SEO includes quite a long checklist of tasks to do. A few years ago, it was mostly about meta tags, over-optimized content and headlines. If you want to learn SEO in 2020 you’ll have a lot more fun with the on-page stuff. Let’s dive in.
Search engine algorithms have come a long way and become more sophisticated from the times when content, titles and descriptions stuffed with keywords were enough to achieve high rankings in search results.
If you want to learn SEO, you can’t get stuck in the past. One of the biggest improvements of search engines is that they consider the human factor, in other words, the user engagement.
Meta tags
Meta tags are a part of the HTML code. They describe website’s content. The most important are meta titles and meta descriptions.
For detailed information, make sure to read the definitions and advanced optimization tips in our SEOpedia both for title tags and meta descriptions.
They aren’t as important as they used to be from the technical point of view.
Don’t get confused by bloggers saying that title tags and meta descriptions aren’t important at all. On the other hand, keep in mind that Google algorithm changes titles and descriptions to better indicate their relevance to the search query in case your copy doesn’t match enough.
There are many tools and plugins (e.g. Yoast for WordPress) analyzing your content in terms of focus keyword usage in meta title, meta description, headings, overall keyword density, alt image attributes and others.
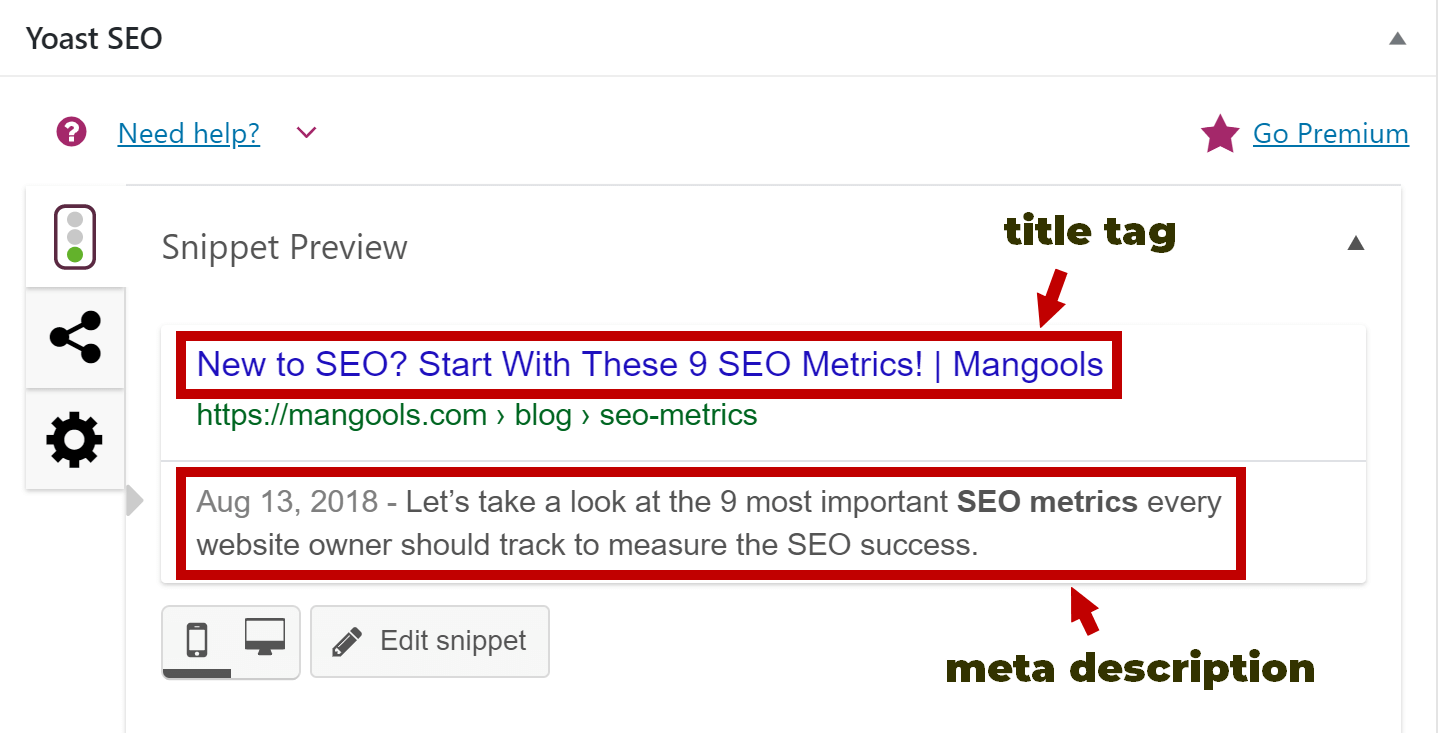
They offer a lot of hints, yet can hardly follow Google’s algorithm focusing when it comes to human factor. Make sure that you consider both technical points of view and user experience when creating meta tags.
On-page SEO checklist
Let’s start with the things you can do in WordPress or any other content management system.
1. Find out what people are searching before you start writing
Do you plan to write about a topic that people search for? Are you sure your point of view is different, unique? Can you offer a new added value to the topic? Is your timing right?
These are the major questions before you start writing and it doesn’t matter whether it’s a blog or a product landing page. There are many ways how to find out. Keyword research is an inevitable part of it. We talk about how to do keyword research in the 5th chapter.
2. Title tags and headlines
Create an appealing title tag, meta description and headlines. Keep in mind what we mentioned earlier. Your main focus keyword should still be there, so users know what is your website about. Use the meta description as a great opportunity for the call-to-action (CTA) emphasis.
Persuade both users and search engines that your website is the one to be clicked on.
Once again, think of the user engagement, so don’t overact by using cheap or too cheesy words. Look at your competitors, analyze what works for them and build your own strategy.
Quick tips for title tags and headlines:
- Google will show the titles if they’re up to 70 characters and meta descriptions up to 155 characters (updated on May 2019).
- Make sure to use correct
,
,
, … structure for good readability and structure.
- Check the search results preview in tools such as our SERP simulator (screenshot below), SEOSiteCheckup, or WordPress plugins.
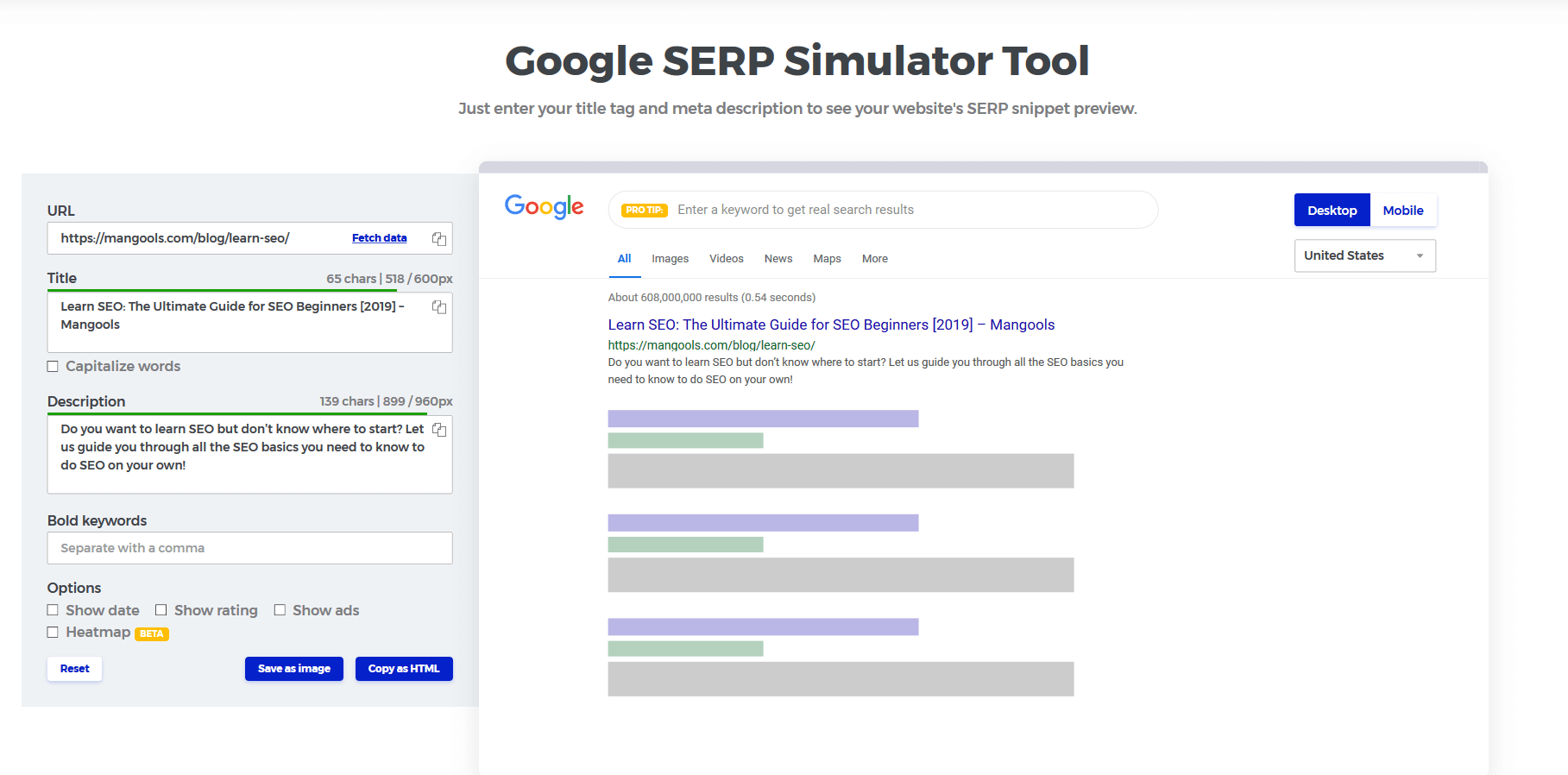
3. Use SEO-friendly URLs
Avoid using auto-generated URLs with figures and characters:
www.example.com/2017/post318e7a349f6
Use URLs corresponding to your content and its title:
www.example.com/how-to-bake-pizza
If you use WordPress, you can set permalinks in the common settings.
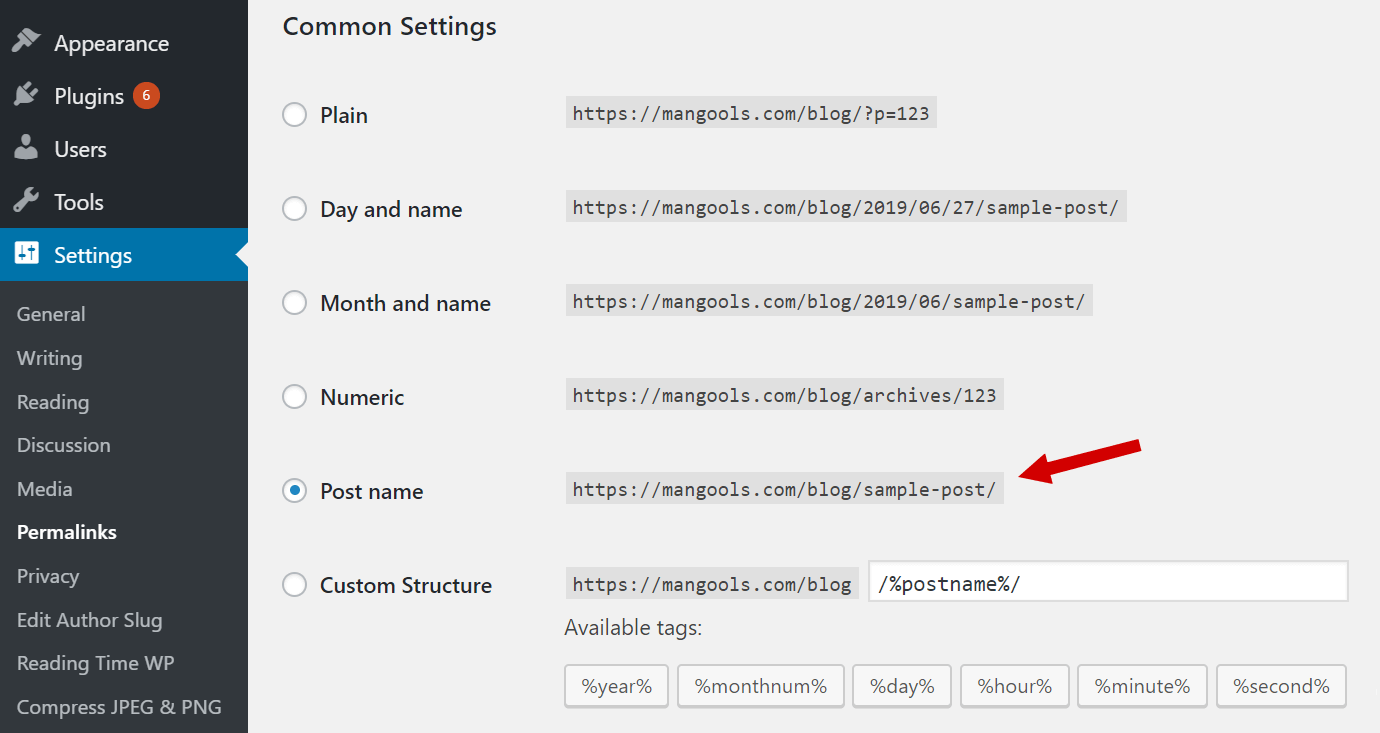
SEO specialists and bloggers say that short URLs ranks better in Google. We think it’s a matter of the user experience. Of course, this doesn’t mean a 20-word URL is alright.
4. Multimedia
Do you want to engage your visitors? Use images, infographics, charts and videos. They lead to lower bounce rates and higher engagement. Some things have to be written in the good old-fashioned way but multimedia are a must.
Video streaming has been one of the hottest marketing trends over the last couple of years. Furthermore, they motivate people to like, share or comment your content.
Quick tips for multimedia:
- Optimize images by using relevant file names (how-to-bake-pizza.jpg), alt image attributes and file size.
- Embed interactive multimedia such as videos or charts.
- Don’t forget to include transcripts so you don’t lose important keywords (search engine crawlers can’t “read” the video).
5. Outbound and internal links
Using outbound links gives a relevancy signal of your topic to Google. Make sure to link to relevant and authoritative sources.
Internal links are a perfect way to promote your other articles or website sections. It makes easier to visit them and leads to higher engagement. Internal linking also helps Google bots to understand the website structure.
Quick tips for outbound and internal links:
- Outbound links may not directly improve your rankings, yet it is highly advisable to use them.
- Use up to 2-3 internal links, depending on the content length.
- Search engine crawlers scan these links, so don’t try to cheat and watch out for broken links.
- Follow the topic cluster model for internal linking.
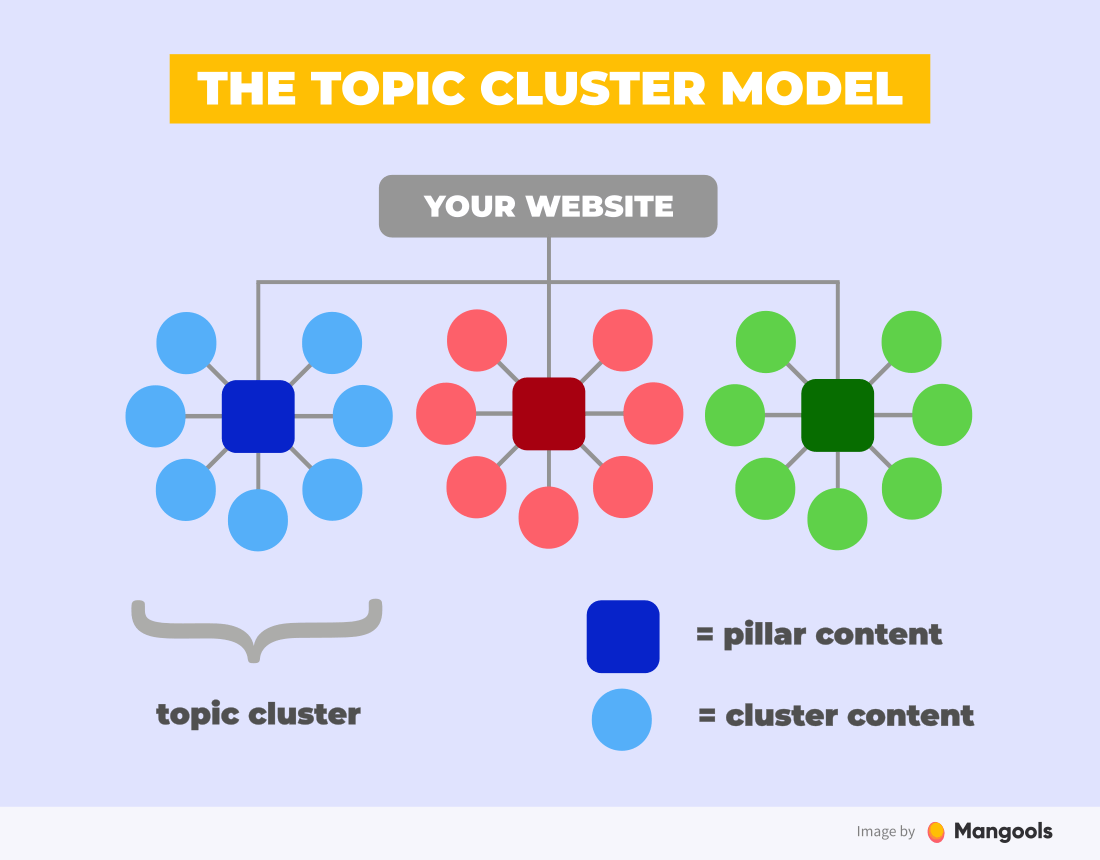
One of the great ways to interlink your content is to follow the topic cluster model
6. Let people engage
Great content shares itself. Yes, maybe in the past. People are lazy these days so the share buttons should always be on your website. According to BuzzSumo, social sharing dropped by half since 2015.
Besides Facebook, Twitter or LinkedIn, consider adding specific and topic-related social networks, such as Reddit, Pinterest and many others.
FREE Download (.pdf)
Technical on-page SEO checklist
We can classify technical SEO as a part of the on-page SEO that deals with more technical stuff. It usually requires at least some development skills or a web developer. But don’t get scared too much, there are many things you can do easily in WordPress .
These are the most important technical SEO factors you should focus on:
1. Search Console
Connecting your site to the Google Search Console (former Webmaster tools) is one of the SEO basics. It helps you to monitor and maintain your site’s presence and performance in Google Search.
The Search Console helps you analyze your keyword rankings, CTRs, possible Google penalties and many other useful data for technical SEO.
Other features include content mobile usability, choosing what you want to be indexed and what not, site errors, structured data errors and links.
Quick tips:
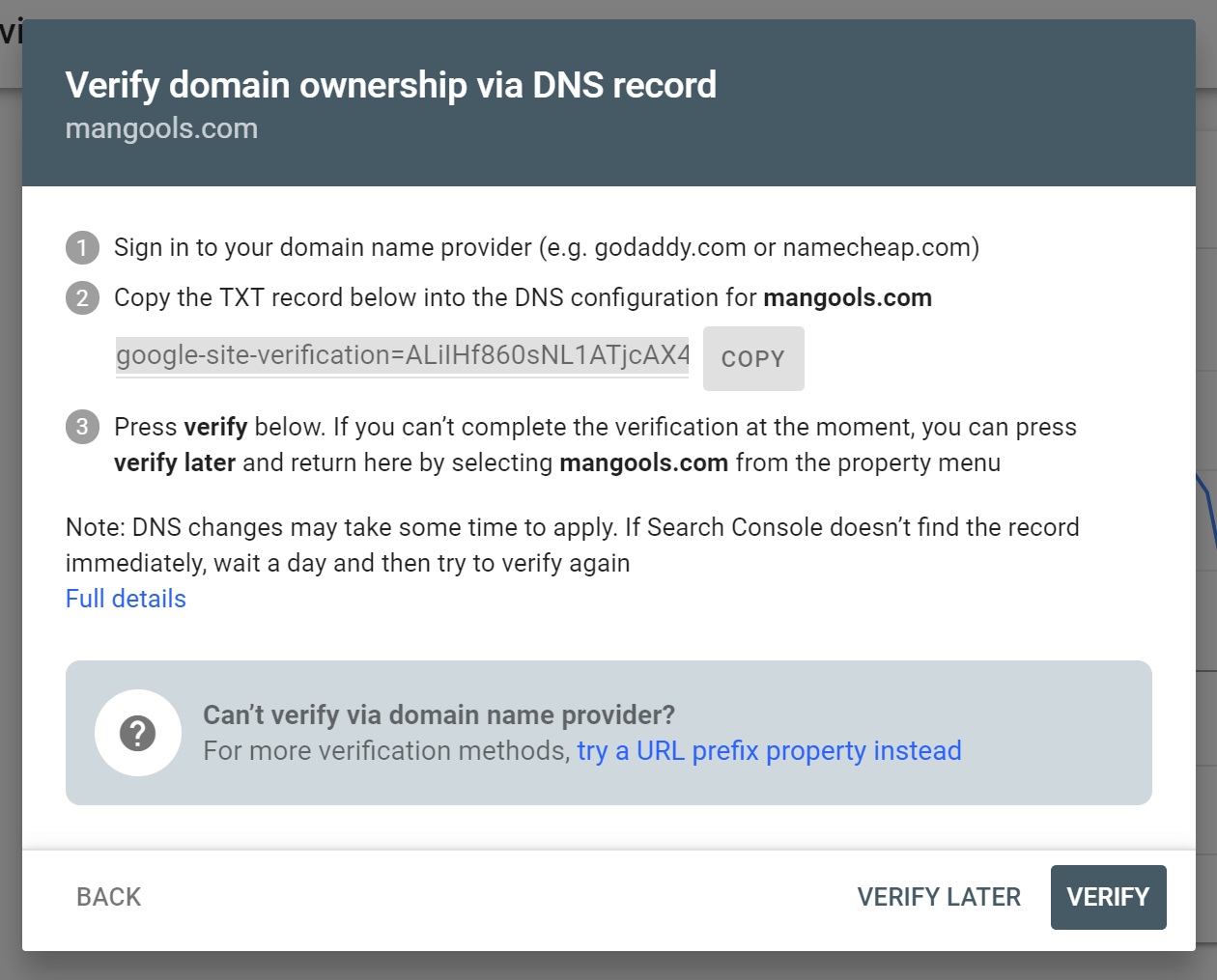
How to verify your property (website) in the Search Console
2. Website speed
Website speed is one of the ranking factors so you should always aim to improve it. It’s known that 50% of web users expect a site to load in 2 seconds or less. If it doesn’t load in 3 seconds, they will leave.
Quick tips:
- Test the speed in PageSpeed Insights.
- Optimize images, enable GZIP compression, HTML compression, JS and CSS minification and try to decrease server response time.
- Quality web hosting plays a big role in the website speed, so make sure to select a trustworthy provider.
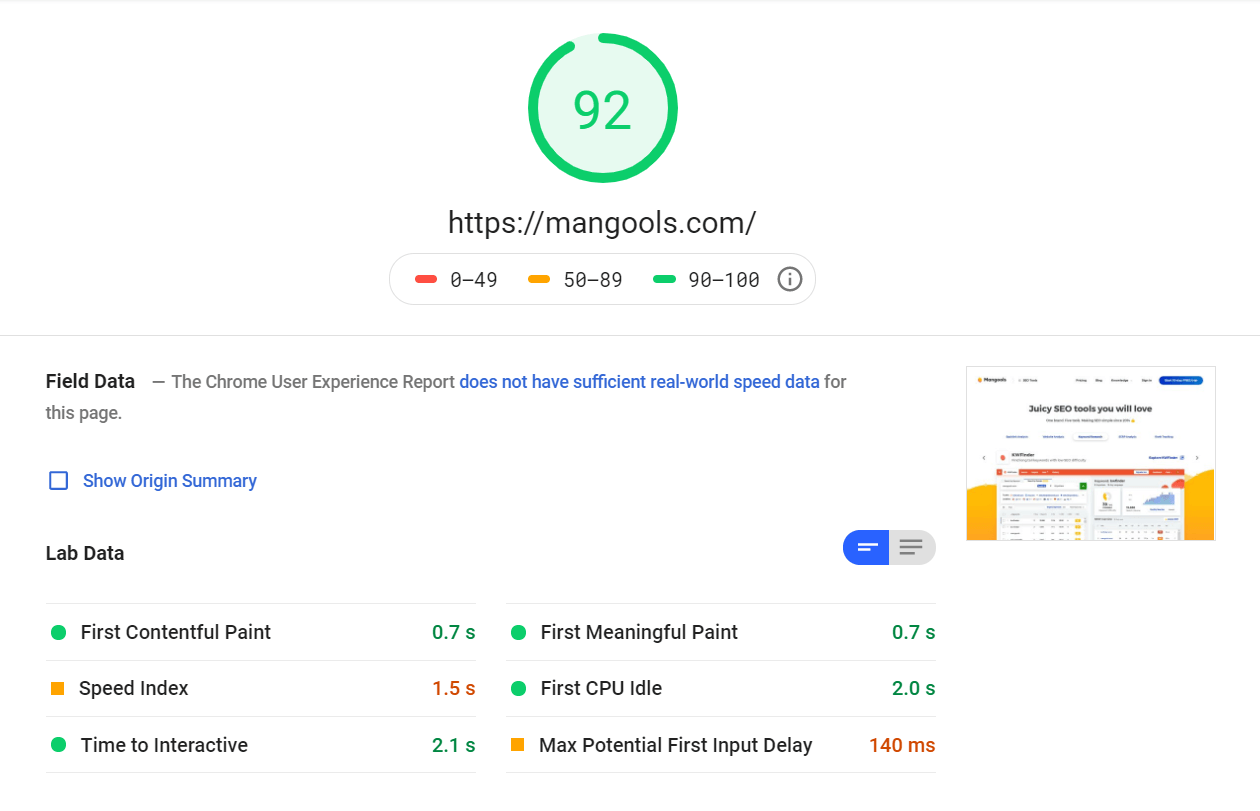
Testing site speed of your website
3. Mobile optimization
Mobile optimization is a must. The world is shifting from desktop to mobile. In fact, running a website that is not mobile-optimized will negatively influence your rankings.
Google started rolling out the mobile-first indexing in March 2018. The mobile-first indexing means that Google will use the mobile version of your website for indexing and ranking.
Quick tips:
- Test the responsivity of your website in the Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Monitor your keyword rankings in mobile search results.
- Make sure the mobile version of your website works like a charm.
You can also consider the AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages). It’s an HTML code extended with custom properties that enable to render static content faster. In 2017, it was one of the main Google’s projects of mobile search. We’ll see if there’s any future for this.
4. Sitemap
A sitemap helps search engines to crawl your content. It’s a file where all website sections are listed. It’s good to have one when you run a large website with a complicated structure or when you use rich media content.
Having a sitemap doesn’t mean your rankings will improve. According to Google, it’s a benefit but you’ll never be penalized for not having one.
Quick tips:
- Not all websites need a sitemap.
- There are more types of sitemaps than just the XML sitemap.
- The Sitemap shouldn’t contain more than 50,000 URLs and cannot exceed 50 MB.
- Place the sitemap in the root directory of the website:
https://example.com/sitemap.xml
5. Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a file that tells crawlers which website sections you don’t want them to be accessed. It’s located in https://example.com/robots.txt and it’s public.
It’s handy when you don’t want some scripts, unnecessary files or images to be indexed.
robots.txt syntax:
User-agent: * (e.g. Googlebot) Disallow: / (e.g. /images/pizza.png)
Quick tips:
- Don’t use robots.txt to hide content from search engines.
- Crawlers or malware robots should not be able to violate robots.txt
FREE Download (.pdf)
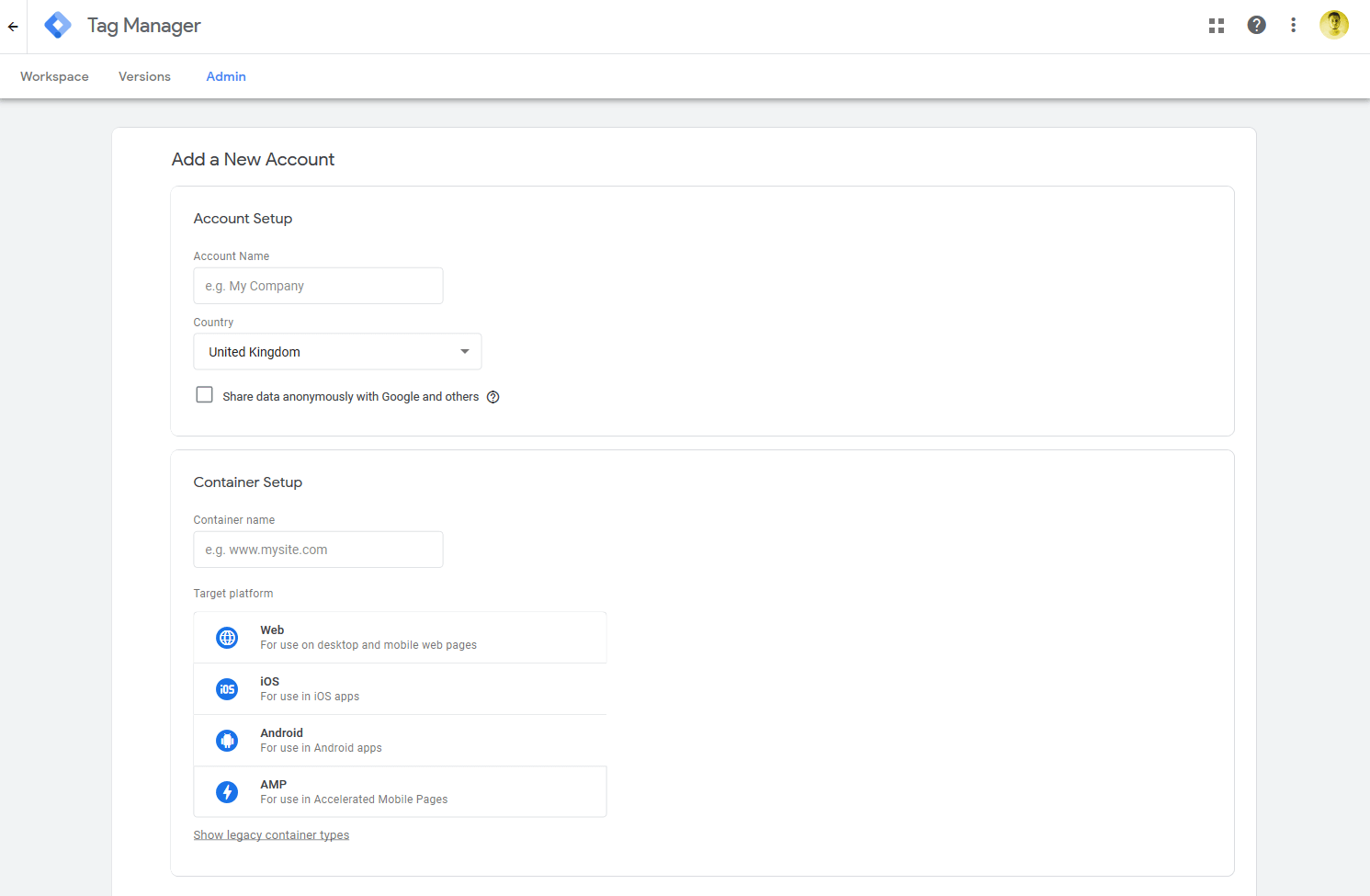
Further technical SEO hacks
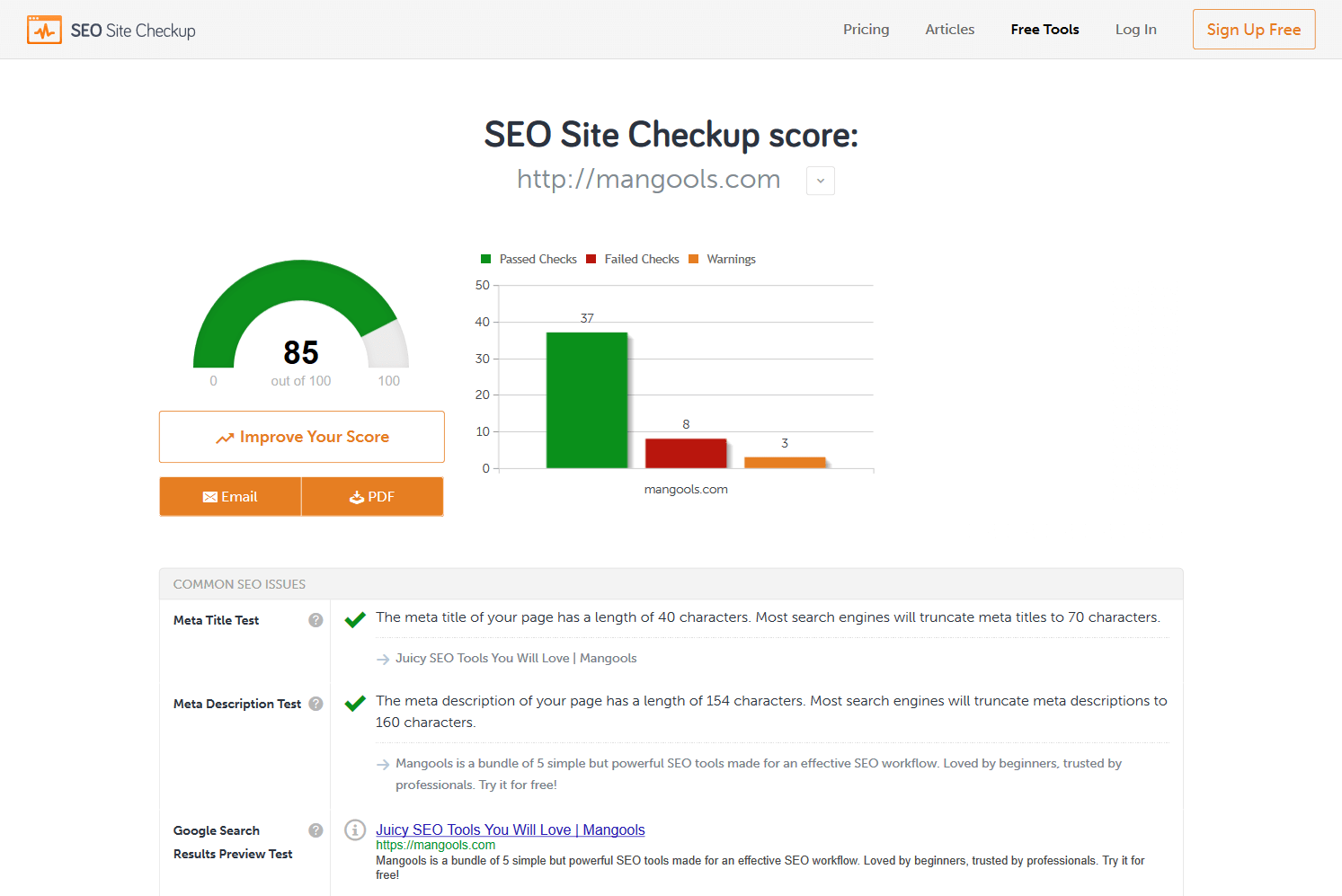
There are many SEO hacks that will boost your website performance. First, start with the analysis of the current state. It will help you find the opportunities.
SEOSiteCheckup is a great tool for on-page SEO analysis. You can analyze one URL per day and download a PDF report without registering.
Set up Google Tag Manager for advanced tag management, so you don’t need any assistance from web developers.
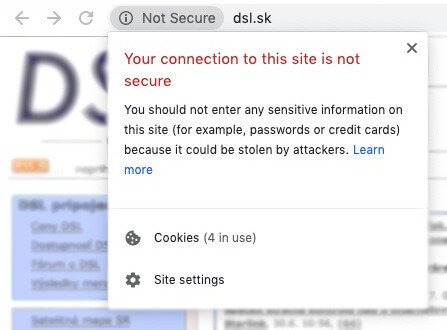
HTTPS vs. HTTP: Back in 2014, Google announced they will boost rankings of HTTPS/SSL websites. Today, we know that it’s a lightweight ranking factor influencing a small percentage of search queries.
However, security is a strong psychological factor. Google Chrome, for example, labels a website that is not encrypted with SSL as “not secure”, which influences the user engagement.
URL/IP canonicalization: IP canonicalization is important when a website is indexed under both its IP address and domain name. URL canonicalization means that:
https://example.com and https://www.example.com/ should resolve to the same URL

Chapter 4
Are content & SEO two independent terms or one ideal couple? A lot of marketers used to think that they are separate players. Let’s find out how you can benefit from their synergy.
There was a popular myth among some marketers that perfect content doesn’t need SEO. The truth is they were wrong. And we’ll show you why.
Seriously, can you imagine high-quality content without on-page optimization or without a single backlink? Likewise, can you imagine a perfectly optimized website packed with content that no one would read?
Your content creation strategy must be part of a broader SEO strategy.
Some people still believe, that:
- SEO is for search engines
- Content is for human beings
They’re wrong! Content & SEO overlap. You simply have to create unique content and optimize it for search engines and people at the same time.
What content should I create?
This is the first and most important question. The answer (at least in theory) is simple: “Be unique”. Creating original, thought-provoking and engaging content is a great start. Content and SEO must go hand in hand from the beginning. You can choose from various content types:
Blogs
Blogs are very popular, especially in the last years. A good blog is a great source of user engagement not only for bloggers but also for e-commerce websites, SaaS businesses or professional service providers.
Blogging is also a way how to earn money by doing what you love (travel bloggers, marketing bloggers, etc.). Unique blogs with in-depth articles, guides and how-tos can make you a respected influencer in the industry.
Quick tips:
- Stand out from the crowd, be original
- Conduct your own research and use unique data
- It’s not about length, it’s about quality and added value for readers
- Be consistent to create a strong personal brand
- Cooperate with companies and influencers
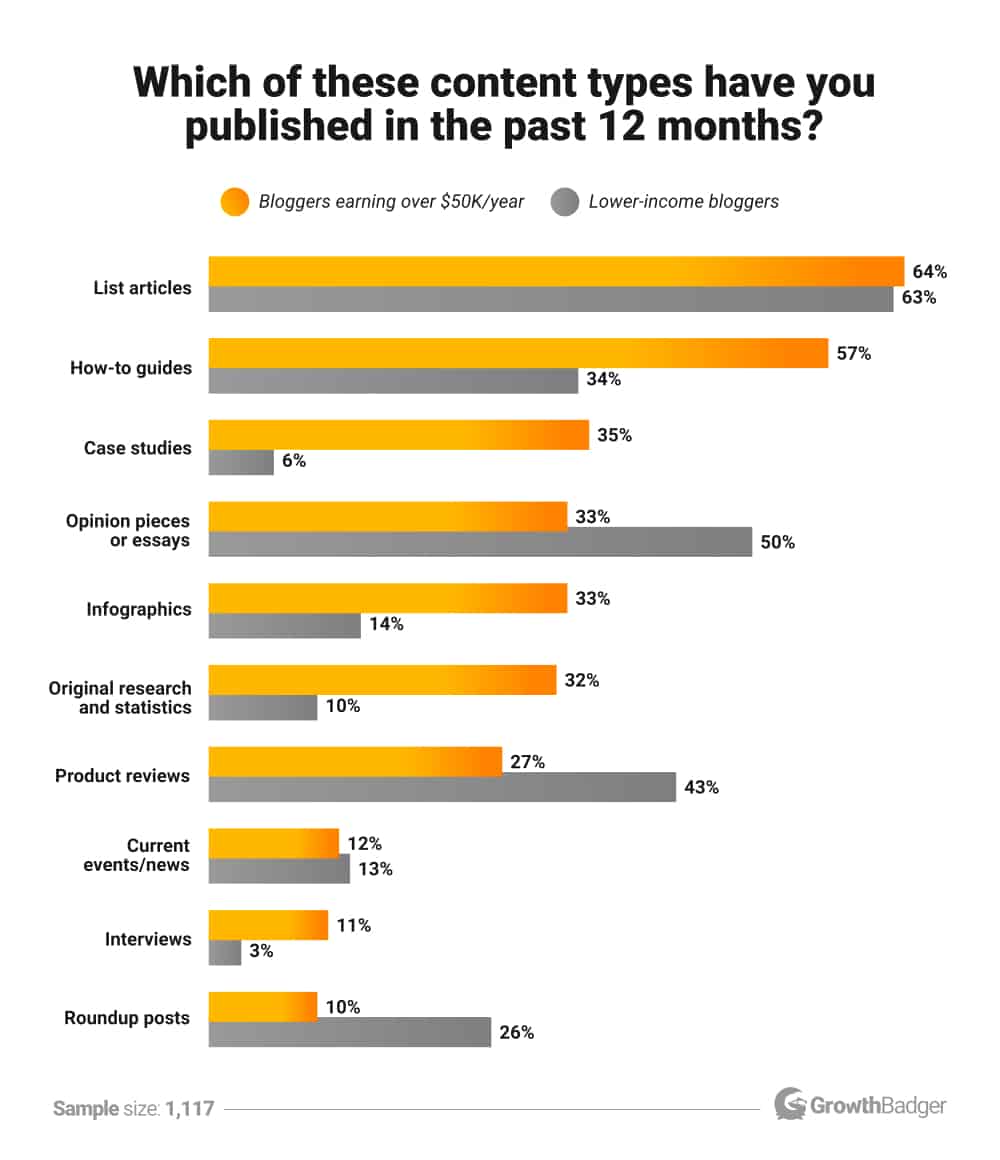
You can be really creative with the types of content you publish on your blog. Here are the most common ones (based on a survey by GrowthBadger):
Product pages
Quality product pages should be the top priority of every online business. They are often used as landing pages for PPC campaigns, including the AdWords remarketing or paid social media.
Quick tips:
- When it comes to eCommerce, simplicity is a must so clearly describe the product, how much is it and how to buy it (CTA)
- Use professional photos of products and write appealing copy
- Website speed and UX are more important than ever
Reviews
Do you want to be an influencer? Writing a review is nothing new but in the world of the internet, everything can be reviewed. You can write reviews of tools, films, bars, restaurants, electronics, you name it.
If you manage to become a trustworthy influencer, you will form people’s opinions and profit from sponsored reviews. Reviews are an inevitable ingredient of the influencer marketing.
Quick tips:
- Choose one specific topic
- Don’t sell yourself out just because some company pays well for a 5-star review
- Create your own standard of what is superb or poor
- Consistency is the key to become a strong brand
Case studies and original research
Tell the world about how you do things, share interesting data you collected, reveal what is your customer satisfaction strategy or how you failed when launching a new product. Do experiments, test various myths in your industry.
Probably the best thing about case studies is that they are always unique and bring new information for readers.
Quick tips:
- Take your time, do your research, prepare enough original data and be honest (don’t lie)
- If you are writing about your business, show the humans behind the company
- Don’t be shy, people aren’t interested in dull success stories
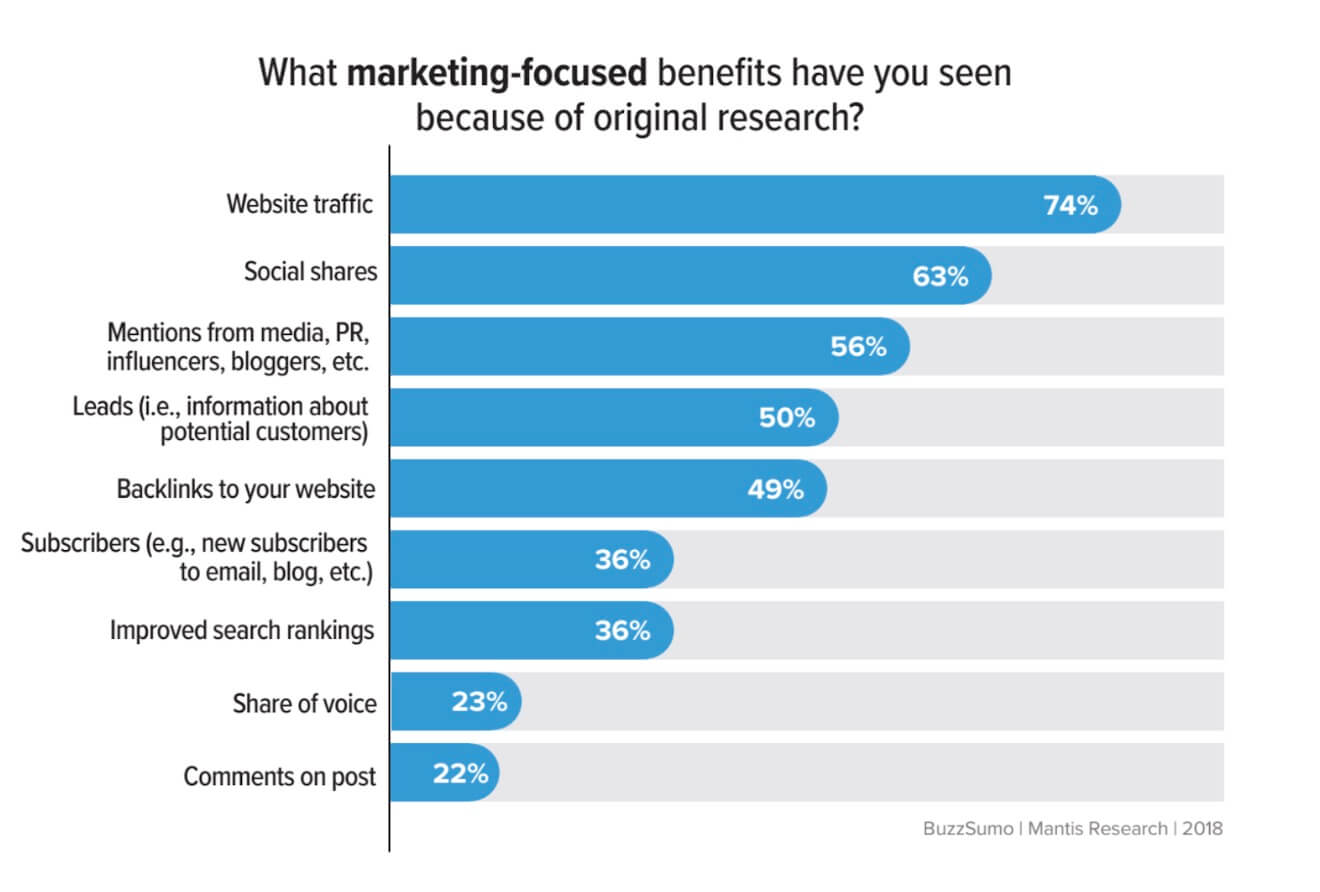
Check this survey on the benefits of publishing original research by Buzzsumo:
Infographics
Everyone likes them! They’re easy to share and download. However, authors frequently use them as a text substitution. Infographics then end up as complicated images with a bunch of copy, so they lost the potential.
Creating infographics is about making information nice and easy to read.
Quick tips:
- Infographics still have a great sharing and linking potential so make sure to play with both data and design
- Use only the most important data
- Create a story, add charts or pictures
- When uploading infographics as pictures, don’t forget to write a transcript because crawlers cannot “read” the text in the image
Guides, how-tos, tricks & tips
Many times, guides are published as a part of blogs. The “… guide” and “How to …” are attractive keywords. You can write guides or how-tos, but keep in mind that there are already thousands of them.
Don’t copy others, provide different tricks & tips than your competitors.
Quick tips:
- Record your own videos, or at least use custom screen recordings and screenshots
- Outreach the product owner or seller to possibly get a backlink or share on their social profiles
- If you are writing a guide on your own product, put the guide on the product landing page to get additional traffic and an internal backlink
Top lists
Another popular form of written content. There are thousands of top lists out there so think wisely about the topic.
Writing lists is an opportunity to include downloadable items to collect leads, to earn valuable comments and to create a buzz thanks to social shares and backlinks.
Quick tips:
- The headline says everything about the post
- Stress extraordinary facts
- Keep the structure simple
- Use proven data sources
- Ask the readers to suggest other items to your list in the comments
Interviews
Getting unique information and opinions from an industry guru is excellent! It helps to build credibility, traffic, social shares and backlinks.
What’s more, interviewees with large audience generate high traffic for free if they share the interview. You can write, record a video or a podcast.
Quick tips:
- Try to interview a thought leader (famous person in the industry)
- Set a clear structure of the interview
- Questions should flow naturally
- Allow some space for the interviewee, readers are curious about their thoughts
Videos
Higher engagement, social shares, likes, backlinks, more leads and conversions. These are the biggest benefits of using video content. Videos can increase conversion rates by 80%.
Quick tips:
- Write a script, proofread and practice the script
- Prepare some budget either for hardware and editing software or for hiring a professional video maker
- Include transcript
- Formulate a marketing plan or at least plan the basic promo activities to justify the time and money you’ve put in
Of course, you don’t always need to create your own videos. Make your post more interesting by sharing or embedding the video by an industry expert! It can enrich your content and make the reader stay longer on your website.
And in order to practice what we preach, here’s a video on content marketing strategy by Julia McCoy:
Ebooks
Ebooks are usually used for lead generation. Maybe more in the B2B industry but there are still many B2C websites that require an email address to download an ebook.
No one gives you the contact details just like that. You need to give readers a good reason. Ebooks usually come in PDF and contain a long piece of content.
Quick tips:
- Write it as a proper book: you need a killer topic, title, preview, credible author, proper proofreading and catchy design
- Motivate users to download: use ebooks with unique data and special tricks that can’t be found on your website or when compared to competitors
What’s the ideal blog post length?
A few years ago, long posts stuffed with keywords ranked on the top positions easily. Somehow, it got to the point, where it looks like there are hundreds of almost identical articles with the same keywords.
Creating content for the sake of content doesn’t work anymore.
If you write an article, you need to keep reader’s attention. It starts with the title, first paragraph, content type and most importantly the overall content structure. Use
, <h1, h2, h3, …> and other HTML tags correctly.</p>
<p>When it comes to time, posts with a 7-minute reading time are ideal according to <a href="https://medium.com/data-lab/the-optimal-post-is-7-minutes-74b9f41509b#.w0vqlrwer" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Medium</a>. When it comes to SEO, there are many studies. Most of them prove that longer posts rank slightly better.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/contentlengthbyrank-seo-guide-for-beginners.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/contentlengthbyrank-seo-guide-for-beginners.png" alt="Content length case study" width="1280" height="931" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/contentlengthbyrank-seo-guide-for-beginners.png" /></a></p>
<p>The graph with the correlation between the content length and organic positions, based on the <a href="http://www.canirank.com/blog/does-long-content-rank-better/" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">study by Can I Rank.</a></p>
<h2>What about duplicate content in my other articles or website sections?</h2>
<p>Sooner or later, we all get to the point where we need to repeat a few words we have written somewhere else on our website.</p>
<p>If there’s too much duplicate content across your website, you can use <b>301 redirects</b> or <b>rel=”canonical”</b> link element. You can find out more on <a href="https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/66359?hl=en" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Google Search Console help pages</a>.</p>
<p>Keep calm if you don’t plan to copy lines of text. Google algorithm differentiates whether you do it on purpose or as a natural part of your new content.</p>
<p>Just in case you think of copying someone else’s content, you can stop reading this SEO guide. It’s plagiarism and we’re strongly against it. The risks, not to mention the costs, of being a copycat are excessive. Google will penalize and skip your website from the search results.</p>
<p>A popular tool to detect the plagiarism is <a href="https://copyscape.com">Copyscape</a>. All you need to do is to enter the URL of the post.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/copyscape.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/copyscape.png" alt="copyscape screenshot" width="1262" height="592" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/copyscape.png" /></a></p>
<p>Creating great content starts with proper research. Think of the topic, do keyword research, ask your friends, conduct polls on Facebook or anywhere else.</p>
<p>Once you choose the topic, scan the market and carefully read all top ranking websites. Don’t copy them, try to create your own unique content and optimize it perfectly. Right after that, you can start promoting it.</p>
<p><img decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-5.png" width="400" alt="" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-5.png" /></p>
<p> Chapter 5</p>
<p>Keyword research is one of the basic SEO tasks. In this chapter, you will learn how to find your niche and how to find profitable keywords you can rank for.</p>
<p>Creating content without keyword research doesn’t pay off. The content without proper optimization won’t rank and the website traffic will be low. You simply have to know what keywords to target to generate enough quality traffic.</p>
<h2>Where to find keywords?</h2>
<p>There are various ways to find keywords.</p>
<p>Your first task is to come up with the seed keywords – phrases you’ll use as the stepping stone to finding more keyword ideas. If you run a coffee blog, simple phrases such as <em>“coffee beans”</em>, <em>“coffee machines”</em> or <em>“espresso”</em> will work great.</p>
<p>The classic ways to look for keywords:</p>
<h3>Google suggestions</h3>
<p>Google offers many keyword suggestions directly in the SERP. Features such as Google Autocomplete, People Also Ask or Related Searches can be a great source of keyword ideas.</p>
<p>With the autocomplete feature, you just need to write your seed keyword into the Google search and the suggestions will appear automatically.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/autocomplete.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/autocomplete.png" alt="Google autocomplete" width="1060" height="757" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/autocomplete.png" /></a></p>
<p>You can combine your seed keyword with different letters from the alphabet to find more autocomplete ideas (e.g. <em>email marketing a</em>, <em>email marketing b</em>,…)</p>
<p>Here’s another example of keyword ideas that can be found in the Google results page:</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/related-to.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/related-to.png" alt="Google Related Searches" width="1245" height="821" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/related-to.png" /></a></p>
<p>All the suggestions based on the real search queries used by people all over the world.</p>
<h3>Keyword tools<br /></h3>
<p>There are many free keyword tools that can give you hundreds of keyword ideas based on a single seed keyword. One of the most popular ones is Google Keyword Planner although it’s main focus is keyword research for PPC ads.</p>
<p>Another popular free tool is <a href="https://answerthepublic.com">AnswerThePublic</a>. It automatically generates hundreds of Google autocomplete suggestions.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/answerthepublic-3.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/answerthepublic-3.png" alt="AnswerThePublic 2" width="889" height="889" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/answerthepublic-3.png" /></a></p>
<p>Of course, free tools are very limited in their features. They offer many keyword suggestions, but what to do with 500 keyword ideas?</p>
<p>The professional paid keyword tools offer other useful SEO metrics and insights to evaluate the keywords and pick the best ones. Besides, they save you a lot of time a give you a competitive advantage.</p>
<p>Here is a screenshot from the keyword tool KWFinder:</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/difficulty-2.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/difficulty-2.png" alt="KWFinder keyword difficulty" width="1294" height="730" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/difficulty-2.png" /></a></p>
<p>Besides keyword suggestions, it calculates the difficulty of ranking for the keywords as well as SERP for each keyword to help you estimate your chances and analyze the competitors.</p>
<p>You can also look for the keywords your competitors rank for by simply typing their domain.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/search-by-domain.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/search-by-domain.png" alt="search by domain" width="942" height="875" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/search-by-domain.png" /></a></p>
<p>You may think: <em>Do I need a paid keyword tool?</em> My rule of thumb is this: If you make money from your website in any way, then a quality keyword tool is a great investment that will pay off sooner or later.</p>
<h3>Other platforms</h3>
<p>You can look for keyword ideas almost anywhere. Focus on websites people in your niche use to ask questions, communicate and share ideas.</p>
<p>Some of the most popular platforms to find keyword ideas:</p>
<ul>
<li>YouTube</li>
<li>Reddit</li>
<li>Quora</li>
<li>Wikipedia</li>
<li>Forums</li>
<li>etc.</li>
</ul>
<h2>Keyword metrics</h2>
<p>In the past, content creators did keyword research only to find the keywords with high search volumes. They stuffed them into content to trick the search engine algorithms and ensure high rankings in organic search. This no longer helps because keyword research has become a lot more complex!</p>
<p>These days you have to work with more metrics, consider the Google RankBrain algorithm and the actual SERP you plan to rank in.</p>
<p>Relevant keywords with high search volumes and low keyword difficulty – an ideal combination of the three most important factors of keyword research.</p>
<p>We call it The tripod rule of keyword research – these three factors represent the three legs. As soon as you take one of the legs, the tripod will collapse.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/the-tripod-rule-1.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/the-tripod-rule-1.png" alt="the tripod rule of keyword research" width="1199" height="811" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/the-tripod-rule-1.png" /></a></p>
<p>Unfortunately, it is not always that easy and you need to look for a balance between these factors.</p>
<h3>Long tail keywords vs. search volumes</h3>
<p>Start by looking for the long tail or middle tail keywords.</p>
<p>Long tail keywords have lower search volumes but there are thousands that represent the opportunity for you. Count them up and you’ll see their enormous potential.</p>
<p>Visitors who find you via long tail keywords will engage with your content a lot more and their conversion rates are higher. It’s because the query is specific enough to find relevant results. And you want to be at the top of these relevant results.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/long-tail-short-tail-1.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/long-tail-short-tail-1.png" alt="long tail vs. short tail keyword" width="1100" height="868" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/long-tail-short-tail-1.png" /></a></p>
<p>The biggest con of long tail keywords is their search volume. Sometimes, it may be as low as 100 searches per month. That’s why you need to find the right balance and the metric called the keyword difficulty will help you to do achieve it.</p>
<h3>Keyword difficulty</h3>
<p>Once you find keywords you want to rank for, you’ll need to evaluate how hard it will be. The keyword difficulty is a very useful metric that will help you with it.</p>
<p>The value is usually indicated on a scale from 0 to 100. The higher the score is, the harder it is to rank on the 1st SERP for the keyword.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/difficulty-ranges.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/difficulty-ranges.png" alt="keyword difficulty ranges" width="1012" height="721" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/difficulty-ranges.png" /></a></p>
<p>There are many keyword research tools on the market calculating the keyword difficulty. The values may vary – you can see score 30 in one tool and 50 in another one for exactly the same keyword.</p>
<p>That’s because the calculations are based on slightly different metrics and algorithms. The important thing is to compare the results within one tool.</p>
<h3>Search intent</h3>
<p>SERP analysis is a very important part of keyword research. It helps you to find out whether:</p>
<ol>
<li>You are able to compete with websites in the 1st SERP</li>
<li>The search intent behind the keywords you want to optimize for</li>
</ol>
<p>By looking at the SERP you can identify what’s the intention behind the search query. When you are searching for a <em>“homemade pizza recipe”</em>, you probably don’t want to buy a pizza.<br />Always keep this in mind so you won’t end up optimizing for wrong keywords.</p>
<p>There are 4 different search intent types:</p>
<ul>
<li>Navigational – search for a specific website/brand <em>(“google search console”)</em></li>
<li>Informational – search for general information <em>(“how to make coffee”)</em></li>
<li>Transactional – user wants to buy something online <em>(“buy apple iphone xs”)</em></li>
<li>Commercial – user does the research before purchase <em>(“canon 6d review”)</em></li>
</ul>
<p>We have recorded a video to show you how to find long tail keywords with low SEO difficulty:</p>
<p>If you run a blog about pizza recipes, you don’t need to rank #1 for the keyword <em>“pizza”</em> (with more than 4 millions of monthly searches globally)? Look at the SERP for the keyword:</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/pizza-serp.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/pizza-serp.png" alt="pizza serp" width="1776" height="933" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/pizza-serp.png" /></a></p>
<p>It wouldn’t make sense to be there unless you plan to compete with Pizza Hut or Domino’s. Yes, these kinds of keywords are very attractive but in most cases, they are not relevant to your niche. What’s more, they represent only a few of all the searches across the world. The majority of searches are long tail queries.</p>
<h2>How NOT to do keyword research</h2>
<p>Newbies and impatient content creators usually find a keyword with high search volume in Google Keyword Planner or any other keyword research tool while not thinking about other metrics.</p>
<p>As we have explained above, finding an ideal keyword is not only about search volume.</p>
<p>Another mistake is data misinterpretation. A common example is the “Competition” score in Google Keyword Planner. There’s a confusion between this metric and the keyword difficulty.</p>
<p>The competition in GKP represents the level of competition in Google AdWords. It doesn’t represent how hard it is to rank for that keyword.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/keyword-planner-2.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/keyword-planner-2.png" alt="keyword planner competition" width="1332" height="825" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/keyword-planner-2.png" /></a></p>
<p>Another thing you should avoid at all costs is keyword stuffing. Keyword research is no longer about finding one ideal keyword and using it as much as possible.</p>
<p>Instead, select one focus keyword and use it in:</p>
<ul>
<li>The heading</li>
<li>Title tag and meta description</li>
<li>One of the first paragraphs of the text</li>
<li>A couple of times in the text (depends on the length of the keyword too)</li>
</ul>
<p>Google has evolved and it understands what the content is about. If it is well-written, comprehensive and user-friendly, you may actually rank for keywords you did not even use in your text.</p>
<p>If you don’t believe me, <a href="https://mangools.com/blog/keyword-research/#long-form">check this example</a>.</p>
<p>Instead of using the same keyword over and over again, try to look for LSI keywords.</p>
<p>LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords are keywords that are semantically related to the main seed keyword. They are a great add-on to keyword research.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/lsigraph-semantic-keywords.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/lsigraph-semantic-keywords.png" alt="keyword research semantic keywords seo guides" width="982" height="576" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/lsigraph-semantic-keywords.png" /></a></p>
<p>LSI keywords change all the time based on the current trend. Adding semantic keywords to your content is a good idea. You can use LSIGraph to generate a bunch of beneficial keyword ideas.</p>
<p><img decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-6.png" width="400" alt="" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-6.png" /></p>
<p> Chapter 6</p>
<p>In the 6th chapter of our SEO for beginners guide, we will discuss link building – one of the most important aspects of search engine optimization. Let’s learn how you can build a quality link profile.</p>
<p> <b>Link building is a process of getting links from other websites.</b> From the technical point of view, backlinks are hypertext links that serve as navigation among websites. The links are crawled by search engines which allows them to index the web content.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/backlink-1.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/backlink-1.png" alt="what is a backlink" width="1100" height="809" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/backlink-1.png" /></a></p>
<h2>Why is link building so important?</h2>
<p>Search engines use links to explore new websites and to set the overall ranking of a website in SERP. In other words, they explore new content and determine the authority of a website based on the authority passed from external sources.</p>
<p>This means that a website’s link profile is one of the most important ranking factors.</p>
<p>When Google introduced PageRank in the 1990s, the number of backlinks was used as an important metric of the overall ranking. The more links you earned, the better was your ranking.</p>
<p>As this could easily be misused, several Google algorithm updates focused on penalization of shady link building techniques.</p>
<p>Today, link building is no longer about the number of backlinks, but mostly about the quality and relevance.</p>
<h2>Types of backlinks</h2>
<p>Generally speaking, there are two types of backlinks:</p>
<ul>
<li><b>Do-follow backlinks</b> pass the authority of the linking page to the linked page. This authority is also often called the “link juice”.</li>
<li><b>No-follow backlinks</b> don’t score any points to the linked website. They don’t pass the authority because of the <em>rel=”nofollow”</em> HTML tag that tells crawlers not to count it.</li>
</ul>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/do-follow-no-follow.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/do-follow-no-follow.png" alt="Do-follow vs. no-follow link" width="1100" height="942" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/do-follow-no-follow.png" /></a></p>
<p>In the illustration above, <em>Site A</em> links to both<em> Site B</em> and <em>Site C</em>. But only the link to <em>Site B</em> passes the “link juice”. The other one has a no-follow tag, so no authority is passed to <em>Site C</em>.</p>
<p>No-follow links have no value from the SEO point of view.</p>
<h2>Anchor text</h2>
<p>The anchor text is a visible, clickable part of a hyperlink. It helps crawlers to indicate what the linked page is about.</p>
<p>If more pages link to you with certain terms used in the anchor texts, it may help you rank for these terms in the search engines.</p>
<p><em>Well, then all I need is a lot of backlinks with my focus keyword as an anchor text, right?</em></p>
<p>It’s not that easy. An over-optimized anchor text profile may lead to an algorithmic penalty by Google. It is better to leave the anchor texts to be natural rather than trying to tweak them artificially.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/anchor-text-1.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/anchor-text-1.png" alt="anchor text" width="1100" height="470" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/anchor-text-1.png" /></a></p>
<p>There should be a balance among the following types of anchors:</p>
<ul>
<li>Keywords and phrases <em>(“SEO tools”)</em></li>
<li>Brands <em>(“mangools”)</em></li>
<li>Branded terms <em>(“SEO tools by mangools”)</em></li>
<li>Generic anchors <em>(“page”)</em></li>
<li>Naked URLs <em>(“mangools.com)</em></li>
<li>CTAs <em>(“click here, “read more”)</em></li>
</ul>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/06-anchor-distribution.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/06-anchor-distribution.png" alt="anchor text distribution" width="1898" height="807" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/06-anchor-distribution.png" /></a></p>
<p>Anchor text distribution chart in SiteProfiler</p>
<p>For more detailed information about anchor texts and how to optimize them, check our SEOpedia’s <a href="https://mangools.com/blog/seopedia/anchor-text/" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">article dedicated to anchor texts</a>.</p>
<h2>Quality aspects of backlinks</h2>
<p>Google considers multiple quality aspects of the referring websites:</p>
<ul>
<li>Domain Authority</li>
<li>Page Authority</li>
<li>Other link profile quality metrics</li>
</ul>
<p>There are several metrics by Moz and Majestic which help us to evaluate/approximate these qualities:</p>
<ul>
<li>Moz Page Authority (PA)</li>
<li>Moz Domain Authority (DA)</li>
<li>Majestic Trust Flow (TF)</li>
<li>Majestic Citation Flow (CF)</li>
</ul>
<p>The higher is the value, the higher is the quality of the backlink.</p>
<p>When we take a look at Majestic’s “Trust Flow and “Citation Flow”, we’ll get another evaluation of links.</p>
<p>The first mentioned says that sites closely linked to a trusted seed site can see higher scores, whereas sites that may have some questionable links would see a much lower score. Citation Flow predicts how influential a URL might be based on how many sites link to it.</p>
<h3>Relevancy</h3>
<p>Links referring to a website have to be relevant to its content. A backlink from a clothes e-shop will be useless for you if you write a blog about recipes.</p>
<h3>Link placement</h3>
<p>Links placed in the main articles or sections are better than links in footers and sidebars. Single links tend to be more valuable than sitewide links.</p>
<p>Sitewide links appear on all pages of a website. They are usually in the footer, header, sidebar or blogrolls. Sitewide links are great both for internal and external link building.</p>
<p>They can generate a lot of traffic. Don’t get scared by them but make sure to use only natural links and keep in mind that their SEO potential may be a bit lower when compared to single links.</p>
<p>Besides the aspects mentioned above, we need to consider the freshness of the link, the anchor quality, popularity and social signals.</p>
<h2>Link building strategies</h2>
<p>It’s not easy to acquire a high-quality backlink. The techniques that were the simplest (reciprocal links or directory submissions) do not work anymore, so the SEOs spend a lot of time trying different approaches.</p>
<p>Let’s take a look at what works the best these days:</p>
<h3>Guest posting</h3>
<p>Guest posting is probably the most popular link building technique. The equation is simple: You write a post and publish it on another website. The website will get free content and you’ll get a free backlink. Win-win.</p>
<p>Of course, it all comes down to quality. If you want a good backlink, you need to bring your A-game in terms of the guest post quality. The popularity of this technique means that everyone uses it and there are too many bad guest posts and bad outreach emails. Here’s what you should keep in mind when doing the guest post outreach campaign:</p>
<ul>
<li>Don’t use templates</li>
<li>Be personal</li>
<li>Offer relevant, well-researched topics</li>
</ul>
<h3>Competitors’ backlinks</h3>
<p>A time-consuming but still quite effective strategy is to find what works for the others. Check the websites that link to your competitors, create better content and contact relevant people behind these websites to link to your website instead.</p>
<p>The easiest way to find your competitors’ backlinks is to use a backlink tool such as <a href="https://linkminer.com">LinkMiner</a>. All you need to do is to enter the domain of your competitor and the tools will show you the backlinks they have.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/domain-competitor.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/domain-competitor.png" alt="domain competitor" width="1376" height="914" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/domain-competitor.png" /></a></p>
<p>You can do the same with the specific URL of your competitor. This comes in handy especially when you are looking for the link building opportunities for a specific blog post. All you need to do is to find the top-ranking pages for your focus keyword and analyze their backlinks.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/url-competitor.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/url-competitor.png" alt="page competitor" width="1500" height="1015" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/url-competitor.png" /></a></p>
<p> </p>
<p>Once you find your <a href="https://mangools.com/blog/how-to-find-and-replicate-competitors-backlinks/">competitors’ backlinks</a>, it’s time to analyze the best opportunities. You should consider:</p>
<ul>
<li>Link relevance – Is the link relevant to your content?</li>
<li>Link strength – What is the authority of the linking page?</li>
<li>Chance to replicate the backlink – Will I be able to get the same backlink?</li>
</ul>
<p>The next step is the so-called email outreach – contacting the website owners to replace the backlink of your competitor (also known as <em>The Skyscraper Technique</em>) or add your backlink as an additional resource.</p>
<p>Here are some other popular link building techniques:</p>
<ul>
<li>Content-based link building: Create content that will naturally attract backlinks, social shares and referral traffic</li>
<li>Social backlinks: Share your content on social media, promote it on Facebook, join discussions, comment relevant posts and create connections</li>
<li>Broken link building: Find websites with inactive links and give them your content to link to instead</li>
<li>PR articles written by professionals and published on news portals will give you high-quality backlinks but prepare some budget for this and make sure they are truly relevant</li>
<li>Buying backlinks via paid blog posts</li>
<li>Writing a testimonial for a product with a backlink to your website</li>
<li>Backlinks from forums, Q&A sites, top lists, comments, content aggregators, business listings, etc. <em>(keep in mind that a vast majority of them are no-follow or low-quality backlinks)</em></li>
<li>Grey/black hat techniques such as PBN (Private Blog Network) link building</li>
</ul>
<h2>Black hat techniques and penalties</h2>
<p>Paid backlinks and PBN (Private Blog Network) link are another way to build backlinks but these techniques are considered black hat (or gray hat). Google may detect the pattern and penalize your website.</p>
<p>On the other hand, these techniques work. You just need to be super careful and think about all the possible risks before taking the black-hat path </p>
<h3>Penalties</h3>
<p>Google Penguin algorithm update from April 2012 started to detect and penalize for bad, spammy, or low-quality links.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/06-unnatural-links-f.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/06-unnatural-links-f.png" alt="Google penalty email" width="913" height="966" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/06-unnatural-links-f.png" /></a></p>
<p>Nobody wants to receive one of these</p>
<p>However, if you have spammy or low-quality backlinks you did not create, don’t panic! Google understands that not all bad backlinks were created on purpose and usually, the worst-case scenario is that it will just ignore these backlinks. If you want to be sure, you can still disavow such backlinks in the Search Console.</p>
<h2>Best practices</h2>
<ul>
<li>Do link building regularly, it’s not a one-time effort</li>
<li>Acquire a few high-quality links rather than many low-quality links</li>
<li>Do natural anchor text distribution based on the tips we listed in the “Anchor text” section</li>
<li>Avoid backlinks from spammy websites and networks</li>
<li>Try to acquire backlink placements which could bring you referral traffic as well</li>
</ul>
<p><img decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-7.png" width="400" alt="" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-7.png" /></p>
<p> Chapter 7</p>
<p>UX and SEO are two aspects of digital marketing that go hand in hand. In this chapter, we focus on their synergy to find out how you can improve your rankings by doing a little extra on your website.</p>
<p>If you were starting with SEO in 2008 your main tasks would be <i>stuffing your content with keywords, ideally hidden as white text, doing reciprocal backlink exchanges and creating low-quality content pages for every keyword variation</i>.</p>
<p>Luckily, we are in 2020 where the mentioned techniques don’t work and some of them will grant a penalty for your website.</p>
<p>Let’s read them all again and think as a human being. Did you find any positive value? Nope. That’s exactly what they were meant for: to fool the search engine algorithm.</p>
<p>And here comes user experience (UX) which is on the opposite side of the barrier…</p>
<p>While SEOs need to understand it’s not only about rankings, UX specialists have to admit that user experience kicks in even before using the website. </p>
<h2>User experience. What is it?</h2>
<p>User experience is every user’s interaction with the company, its website or products. <b>It’s the overall experience</b> influencing product development, design, marketing and customer support.</p>
<p>In this SEO guide, we focus on the “online” user experience and its relationship with SEO. UX is no longer only about meeting customer requirements. <b>It’s about going beyond these requirements.</b></p>
<p>You should think out of the box and develop a website that naturally covers every possible need of a customer without bothering him.</p>
<h2><b>UX rules nowadays world</b></h2>
<p>The first and most important part is to understand that <b>UX is a never-ending process of improvements towards customers.</b> It’s a philosophy the company should stick to and develop its website accordingly.</p>
<p>Web UX is a mix of content and technical UX. If we wanted to put it simply, we would say UX is everything. That’s why we need to understand its complexity and influence on everyone inside and outside the company. We’re talking about:</p>
<ul>
<li>Website structure and navigation</li>
<li>Conversion funnel optimization</li>
<li>Easy onboarding process</li>
<li>Page speed</li>
<li>Website responsivity</li>
<li>Content optimization</li>
<li>Content structure</li>
<li>Title tags and meta descriptions</li>
<li>Real-time customer support</li>
<li>Smooth workflow</li>
</ul>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/The-UX-pyramid.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/The-UX-pyramid.png" alt="UX pyramid" width="1024" height="512" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/The-UX-pyramid.png" /></a></p>
<p>The UX consists of both objective and subjective factors.</p>
<h2>UX and SEO challenges</h2>
<p>When we think <i>“UX and SEO”</i> instead of <i>“UX vs. SEO”</i>, we have to cope with challenges every once in a while. Not all of the above mentioned are directly connected to SEO. Let’s take a look at the ones that do.</p>
<h3>Website structure and navigation</h3>
<p><i>Let’s put everything on a single page to ensure smooth UX.</i> This is a valid idea in the UX world. It’s easy and it makes sense. But SEOs know that organic traffic is at least half of the success.</p>
<p>Many visitors should come from the organic search or access the page directly based on their previous actions. Other visitors are referred from various sources such as social media, blogs or PPC campaigns.</p>
<p>Can you imagine a single-page experience for all of these different intentions and search queries? People use Google to find what they want. Your website should be the finding.</p>
<p>When it comes to the website navigation, don’t try to fit all possible landing pages there for the sake of SEO. Having a link to your latest blog post in the navigation indicates Google that the URL is important but it may not be relevant to your website visitors.</p>
<p><b>Example:<br /></b>Our blog used to have a different call-to-action button in the top-right corner. It was designed to convert the readers to our SEO tools users. Not that relevant, right? We decided to add “Subscribe to newsletter” instead. It makes more sense from the UX point of view and gives a chance to work harder on our inbound marketing activities.</p>
<h3>Page speed</h3>
<p><b>The faster is your website, the better is the UX.</b> As we mentioned in the <a href="https://mangools.com/blog/learn-seo/#part3">3rd chapter</a>, page speed is one of the ranking factors. There’s a clear relationship between SEO and UX. This is probably the easiest case to explain.</p>
<h3>Content optimization</h3>
<p><b>Understand the language of a typical searcher</b> and adjust your content to it. In other words, do keyword research and optimize your content accordingly.</p>
<p>The point is to make your content accessible for everyone searching for a product, solution or any information that your website may provide. Of course, <b>don’t forget about search intent</b> all keyword research tactics that we explain in the <a href="https://mangools.com/blog/learn-seo/#part4">4th chapter</a> so you won’t end up optimizing for the wrong keywords.</p>
<h3>Title tags and meta descriptions</h3>
<p>The higher in the SERP you are, the higher possibility you get to be clicked. That’s quick math.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/quick-maths.jpg"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/quick-maths.jpg" alt="quick maths picture" width="504" height="415" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/quick-maths.jpg" /></a></p>
<p>However, if you spoil the title tag and meta description the quick math can go wrong. Your goal is to catch the searcher’s attention by using copy that encourages them to click on your website in the SERP.</p>
<p>There are 3 main elements to consider when creating title tags and meta descriptions:</p>
<ol>
<li><b>SEO</b> – Use the right keywords so crawlers can understand what is the website about and what is the most important content.</li>
<li><b>UX</b> – Give the searchers clear and meaningful information that will motivate them to click because they will find what they are looking for.</li>
<li><b>Marketing</b> – Irresistible copy with a clear call to action leads to higher click-through rates.</li>
</ol>
<h2>How to measure UX and SEO</h2>
<p>From Google Analytics through specialized reports to internal data, there’s a variety of options you can use.</p>
<h3>Engagement and behavior metrics in Google Analytics</h3>
<p><b>“Bounce rate”, “Pages per session” </b>and<b> “Avg. session duration”</b> provide a basic view on user interaction. These metrics are almost in every report in GA, so you can see them for various traffic sources.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/mangools-seo-academy-7-ux-seo-bounce-rate.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/mangools-seo-academy-7-ux-seo-bounce-rate.png" alt="How to measure engagement in Google Analytics" width="480" height="279" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/mangools-seo-academy-7-ux-seo-bounce-rate.png" /></a></p>
<p>Engagement metrics in Google Analytics “Behavior”</p>
<p>The more detailed information is available in the category <b>“Behavior”</b>. The “behavior flow” informs you how visitors interact with various sections of the website. Advanced options let you see reports based on traffic sources, landing pages, campaigns and others.</p>
<p>Though the report is usually based on a small percentage of website visitors, it comes with a piece of handy advice: It tells you <b>how many users went through or dropped-off</b> when visiting that particular section.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/mangools-seo-academy-7-ux-seo-behavior-flow.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/mangools-seo-academy-7-ux-seo-behavior-flow-e1492691179701.png" alt="Behavior flow report in Google Analytics" width="2029" height="836" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/mangools-seo-academy-7-ux-seo-behavior-flow-e1492691179701.png" /></a></p>
<p>Behavior flow report in Google Analytics</p>
<h3>Conversion funnels in Google Analytics</h3>
<p>This report tells you how people interact with the checkout page on your website. Do you have more than one step in the checkout process? In this case, don’t forget to properly set up the goal tracking in the admin menu.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Analytics-goal-funnel-setup.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Analytics-goal-funnel-setup.png" alt="Funnel settings in Google Analytics" width="731" height="676" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Analytics-goal-funnel-setup.png" /></a></p>
<p>Setting up the funnel in Google Analytics</p>
<p>This way, you’ll measure how many people went through all the steps and how many abandoned throughout the process. It can be a registration form, buying process or subscription form on your blog. It’s just another extremely useful information for UX optimization.</p>
<p>If the majority of the website users who visited the checkout process didn’t even fill the first form then you know there’s something wrong.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/mangools-seo-academy-7-ux-seo-conversion-funnels.png"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/mangools-seo-academy-7-ux-seo-conversion-funnels.png" alt="Conversion funnel report in Google Analytics" width="652" height="347" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/mangools-seo-academy-7-ux-seo-conversion-funnels.png" /></a></p>
<p>Conversion funnel report in Google Analytics</p>
<h3>Heatmaps & recordings</h3>
<p>Heatmaps visualize the behavior of website visitors while providing many useful reports. Sophisticated heatmap tools such as <a href="https://www.hotjar.com/" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Hotjar</a> or <a href="https://www.crazyegg.com/" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Crazyegg</a> come with complex analytic solutions but they can be too expensive for bloggers or small businesses. For beginners, a limited free plan by Hotjar or <a href="https://www.ptengine.com/plan" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Ptengine</a> may be a good start.</p>
<p><a href="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/hotjar-heatmap.jpg"><img loading="lazy" decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/hotjar-heatmap.jpg" alt="hotjar heatmap example preview" width="1080" height="722" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/hotjar-heatmap.jpg" /></a></p>
<p>Heatmaps help a lot when it comes to both UX and SEO. The power of heatmaps is in the ability to see <b>exactly where people click, what elements they expect to be clickable, how they scroll, interact, fill in forms.</b></p>
<p>Top-notch heatmap tools include the recordings of the user behavior. Are they worth it? Yes, but not for everyone. Businesses with more complicated (e-commerce) pages (and usually with bigger budgets) should go for it, but there is no point for bloggers to spend hundreds of dollars on these expert tools. Limited free versions should do the job.</p>
<h3>Internal data</h3>
<p>Do you know what’s great about internal data? There aren’t any additional costs. You create these reports packed with useful information all the time:</p>
<ul>
<li>Customer questions</li>
<li>Feedback forms</li>
<li>Comments and reactions</li>
<li>Customer wishes and complaints</li>
<li>Marketing reports</li>
<li>Email responses</li>
<li>Reports from web developers</li>
</ul>
<h3>Testing and site speed</h3>
<p>Testing the website before it’s launched is a must! Beta testers provide a lot of useful information. They’re the first real users. On top of that, you can do some usability testing with colleagues, friends or fans during the development process.</p>
<p>Pay attention to key elements such as page speed, mobile optimization, and other important on-page SEO aspects. The complete list with a downloadable infographic is in the <a href="https://mangools.com/blog/learn-seo/#part3">3rd chapter.</a></p>
<p><img decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-8.png" width="400" alt="" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-8.png" /></p>
<p> Chapter 8</p>
<p>We hope you enjoyed our ultimate SEO guide for beginners as much as we did. Now it’s time to see what you have learned by taking a test and getting our SEO certificate. Fingers crossed! </p>
<p> Let’s dig into what you’ve learned! Test your SEO skills and knowledge you’ve gained in a quick test.</p>
<p>If you successfully pass the quiz, you’ll get the Mangools SEO certificate.</p>
<p>Oops! You haven’t reached enough score to pass the test. Try your luck again. </p>
<h3> 1. What is SEO? </h3>
<p> The process of increasing visibility in search engines through advertising. The process of improving positions in organic search results. </p>
<h3> 2. What is off-page SEO? </h3>
<p> Many activities to improve the domain authority, mostly by getting high-quality backlinks. Improving meta tags, content, images and URL optimization, etc. </p>
<h3> 3. White-hat SEO is: </h3>
<p> A set of unethical practices to improve rankings of a website. A set of ethical techniques sticking to guidelines and rules. </p>
<h3> 4. What is website crawling? </h3>
<p> Pulling out the results from search engines to generate SERP. Scanning the website, its sections, content, keywords, headings, links, images by thousands of small bots. </p>
<h3> 5. What type of search query is “How to prepare for a test”? </h3>
<p> Transactional. Navigational. Informational. </p>
<h3> 6. Are meta keywords still important for improving SEO? </h3>
<p> Yes. No. </p>
<h3> 7. Is using multimedia good for increasing user engagement? </h3>
<p> Yes. No. </p>
<h3> 8. Where would you start looking for technical errors of your website’s appearance in Google search? </h3>
<p> Google Search Console. Google SERP. </p>
<h3> 9. Does mobile-first indexing mean that Google will use the mobile version of your website for indexing and ranking? </h3>
<p> Yes. No, Google will use both desktop and mobile versions. </p>
<h3> 10. “If the content is unique enough, it doesn’t need to be optimized.” </h3>
<p> True. False. </p>
<h3> 11. Can Google bots “read” the content in embedded videos or pictures? </h3>
<p> Yes, it will be indexed. No, we should include a transcript. </p>
<h3> 12. Adding as many popular keywords as possible … </h3>
<p> … will get me to the top of SERP. …won’t help that much anymore. </p>
<h3> 13. Why should we use long tail keywords? </h3>
<p> Because they have huge search volumes. Their search volumes are lower but they’re more relevant and lead to higher engagement. We shouldn’t use them. </p>
<h3> 14. What is a do follow link? </h3>
<p> A link that passes authority to the linked website. A link that helps to get more followers on social media. </p>
<h3> 15. When we do link building: </h3>
<p> We should exchange or buy as many backlinks as possible. We should think of it as a long-term process in which it is good to naturally acquire high-quality backlinks. </p>
<h3> 16. “UX and SEO are two separate players so their synergy wouldn’t bring any positive results.” </h3>
<p> True. False. </p>
<h3> 17. Is there a way to measure UX? </h3>
<p> No, because it’s too subjective. Yes, but only in heatmaps. Yes, in Google Analytics, heatmaps and other reports. </p>
<h3> 18. Sitewide links: </h3>
<p> Are great because you get more backlinks from the same website. Are good but their SEO potential may be lower compared to single links. Are harmful to your website SEO and you should avoid them. </p>
<h3> 19. Should you link to other websites from your article? </h3>
<p> Yes, it is good to link to other relevant sources. No, except for the case when you are paid for the link placement. No, linking to other websites can send the visitor away from your website. </p>
<h3> 20. When doing keyword research, what should we pay attention to besides the search volume and difficulty of the keyword? </h3>
<p> SERP analysis Content length and keyword density Popularity of the keyword on social media </p>
<p> <img decoding="async" data-src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-9.png" width="400" alt="" src="https://mangools.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/chapter-9.png" /></p>
<p> Chapter 9</p>
<p>Besides this SEO guide for beginners, there are many great sources that will help you to learn SEO and improve your optimization skills. We have picked the top ones for you!</p>
<p>SEO is a growing industry and there are literally hundreds of resources you can learn from – wheter you prefer blogs, ebooks, infographics, forums or following the experts. The well-known online marketing company Ignite Visibility even made an <a href="https://ignitevisibility.com/seo-movie/" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">SEO Movie</a>!</p>
<p>Of course, too many resources can be a little overwhelming for an SEO beginner as it may be hard to distinguish quality content from the lousy one. That is why we decided to dedicate the last chapter of our SEO guide for beginners to the best SEO resouces we hand-picked personally!</p>
<p> <a href="https://mangools.com/blog/learn-seo/" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Source</a></p>
</div><div class="post-meta wf-mobile-collapsed"><div class="entry-meta"><a class="author vcard" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/author/admin/" title="View all posts by Grayson Guidry" rel="author">By <span class="fn">Grayson Guidry</span></a><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2020/08/03/" title="6:29 pm" class="data-link" rel="bookmark"><time class="entry-date updated" datetime="2020-08-03T18:29:52+00:00">August 3, 2020</time></a><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2020/08/03/learn-seo-the-ultimate-guide-for-seo-beginners-2020/#respond" class="comment-link" >Leave a comment</a></div><div class="entry-tags">Tags: <a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/tag/digital-marketing/" rel="tag">digital marketing</a><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/tag/facebook/" rel="tag">facebook</a><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/tag/google/" rel="tag">google</a><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/tag/google-local/" rel="tag">google local</a><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/tag/linkedin/" rel="tag">linkedin</a><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/tag/seo/" rel="tag">seo</a><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/tag/yelp/" rel="tag">yelp</a><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/tag/youtube/" rel="tag">youtube</a></div></div><div class="single-share-box">
<div class="share-link-description">Share this post</div>
<div class="share-buttons">
<a class="twitter" href="https://twitter.com/share?url=https%3A%2F%2Flightsforchristmas.co%2F2020%2F08%2F03%2Flearn-seo-the-ultimate-guide-for-seo-beginners-2020%2F&text=Learn+SEO%3A+The+Ultimate+Guide+For+SEO+Beginners+%5B2020%5D" title="Twitter" target="_blank" ><span class="soc-font-icon"></span><span class="social-text">Tweet</span><span class="screen-reader-text">Share on Twitter</span></a>
<a class="pinterest pinit-marklet" href="//pinterest.com/pin/create/button/" title="Pinterest" target="_blank" data-pin-config="above" data-pin-do="buttonBookmark"><span class="soc-font-icon"></span><span class="social-text">Pin it</span><span class="screen-reader-text">Share on Pinterest</span></a>
<a class="whatsapp" href="https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Learn%20SEO%3A%20The%20Ultimate%20Guide%20For%20SEO%20Beginners%20%5B2020%5D%20-%20https%3A%2F%2Flightsforchristmas.co%2F2020%2F08%2F03%2Flearn-seo-the-ultimate-guide-for-seo-beginners-2020%2F" title="WhatsApp" target="_blank" data-action="share/whatsapp/share"><span class="soc-font-icon"></span><span class="social-text">Share on WhatsApp</span><span class="screen-reader-text">Share on WhatsApp</span></a>
<a class="linkedin" href="https://www.linkedin.com/shareArticle?mini=true&url=https%3A%2F%2Flightsforchristmas.co%2F2020%2F08%2F03%2Flearn-seo-the-ultimate-guide-for-seo-beginners-2020%2F&title=Learn%20SEO%3A%20The%20Ultimate%20Guide%20For%20SEO%20Beginners%20%5B2020%5D&summary=&source=Lights%20For%20Christmas" title="LinkedIn" target="_blank" ><span class="soc-font-icon"></span><span class="social-text">Share on LinkedIn</span><span class="screen-reader-text">Share on LinkedIn</span></a>
<a class="facebook" href="https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=https%3A%2F%2Flightsforchristmas.co%2F2020%2F08%2F03%2Flearn-seo-the-ultimate-guide-for-seo-beginners-2020%2F&t=Learn+SEO%3A+The+Ultimate+Guide+For+SEO+Beginners+%5B2020%5D" title="Facebook" target="_blank" ><span class="soc-font-icon"></span><span class="social-text">Share on Facebook</span><span class="screen-reader-text">Share on Facebook</span></a>
</div>
</div> <div class="author-info entry-author">
<span class="author-avatar no-avatar"></span> <div class="author-description">
<h4><span class="author-heading">Author:</span> Grayson Guidry</h4>
<p class="author-bio"></p>
</div>
</div>
<nav class="navigation post-navigation" role="navigation"><h2 class="screen-reader-text">Post navigation</h2><div class="nav-links"><a class="nav-previous" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2020/08/03/marketing-roi/" rel="prev"><i class="icomoon-the7-font-the7-arrow-29-3" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="meta-nav" aria-hidden="true">Previous</span><span class="screen-reader-text">Previous post:</span><span class="post-title h4-size">Marketing ROI</span></a><a class="back-to-list" href="/blog/"><i class="dt-icon-the7-misc-006-1" aria-hidden="true"></i></a><a class="nav-next" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2020/08/03/trump-signs-new-executive-order-targeting-social-media/" rel="next"><i class="icomoon-the7-font-the7-arrow-29-2" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="meta-nav" aria-hidden="true">Next</span><span class="screen-reader-text">Next post:</span><span class="post-title h4-size">Trump signs new executive order targeting social media</span></a></div></nav><div class="single-related-posts"><h3>More Posts</h3><section class="items-grid"><div class=" related-item"><article class="post-format-standard"><div class="mini-post-img"><a class="alignleft post-rollover no-avatar" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/25/etsy-com/" style="width:110px; height: 80px;" aria-label="Post image"></a></div><div class="post-content"><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/25/etsy-com/">etsy.com</a><br /><time class="text-secondary" datetime="2023-10-25T15:35:59+00:00">October 25, 2023</time></div></article></div><div class=" related-item"><article class="post-format-standard"><div class="mini-post-img"><a class="alignleft post-rollover no-avatar" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/25/8721/" style="width:110px; height: 80px;" aria-label="Post image"></a></div><div class="post-content"><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/25/8721/">No title</a><br /><time class="text-secondary" datetime="2023-10-25T09:25:22+00:00">October 25, 2023</time></div></article></div><div class=" related-item"><article class="post-format-standard"><div class="mini-post-img"><a class="alignleft post-rollover no-avatar" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/24/8719/" style="width:110px; height: 80px;" aria-label="Post image"></a></div><div class="post-content"><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/24/8719/">No title</a><br /><time class="text-secondary" datetime="2023-10-24T06:47:51+00:00">October 24, 2023</time></div></article></div><div class=" related-item"><article class="post-format-standard"><div class="mini-post-img"><a class="alignleft post-rollover no-avatar" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/24/8718/" style="width:110px; height: 80px;" aria-label="Post image"></a></div><div class="post-content"><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/24/8718/">No title</a><br /><time class="text-secondary" datetime="2023-10-24T01:17:23+00:00">October 24, 2023</time></div></article></div><div class=" related-item"><article class="post-format-standard"><div class="mini-post-img"><a class="alignleft post-rollover no-avatar" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/23/8717/" style="width:110px; height: 80px;" aria-label="Post image"></a></div><div class="post-content"><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/23/8717/">No title</a><br /><time class="text-secondary" datetime="2023-10-23T09:23:54+00:00">October 23, 2023</time></div></article></div><div class=" related-item"><article class="post-format-standard"><div class="mini-post-img"><a class="alignleft post-rollover no-avatar" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/23/8716/" style="width:110px; height: 80px;" aria-label="Post image"></a></div><div class="post-content"><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/23/8716/">No title</a><br /><time class="text-secondary" datetime="2023-10-23T08:54:00+00:00">October 23, 2023</time></div></article></div></section></div>
</article>
<div class='gf_browser_gecko gform_wrapper gravity-theme gform-theme--no-framework' data-form-theme='gravity-theme' data-form-index='1' id='gform_wrapper_4' >
<div class='gform_heading'>
<h2 class="gform_title">Light Of Christmas Blog form</h2>
<p class='gform_description'></p>
</div><form method='post' enctype='multipart/form-data' id='gform_4' action='/2020/08/03/learn-seo-the-ultimate-guide-for-seo-beginners-2020/' data-formid='4' novalidate>
<div class='gform-body gform_body'><div id='gform_fields_4' class='gform_fields top_label form_sublabel_below description_below validation_below'><div id="field_4_1" class="gfield gfield--type-text field_sublabel_below gfield--no-description field_description_below hidden_label field_validation_below gfield_visibility_visible" data-js-reload="field_4_1" ><label class='gfield_label gform-field-label' for='input_4_1'>Name</label><div class='ginput_container ginput_container_text'><input name='input_1' id='input_4_1' type='text' value='' class='large' placeholder='Name' aria-invalid="false" /> </div></div><div id="field_4_3" class="gfield gfield--type-phone gfield--width-full field_sublabel_below gfield--no-description field_description_below hidden_label field_validation_below gfield_visibility_visible" data-js-reload="field_4_3" ><label class='gfield_label gform-field-label' for='input_4_3'>Number</label><div class='ginput_container ginput_container_phone'><input name='input_3' id='input_4_3' type='tel' value='' class='large' placeholder='Number' aria-invalid="false" /></div></div><div id="field_4_4" class="gfield gfield--type-email gfield--width-full field_sublabel_below gfield--no-description field_description_below hidden_label field_validation_below gfield_visibility_visible" data-js-reload="field_4_4" ><label class='gfield_label gform-field-label' for='input_4_4'>Email</label><div class='ginput_container ginput_container_email'>
<input name='input_4' id='input_4_4' type='email' value='' class='large' placeholder='Email' aria-invalid="false" />
</div></div><div id="field_4_5" class="gfield gfield--type-textarea gfield--width-full field_sublabel_below gfield--no-description field_description_below hidden_label field_validation_below gfield_visibility_visible" data-js-reload="field_4_5" ><label class='gfield_label gform-field-label' for='input_4_5'>Comment</label><div class='ginput_container ginput_container_textarea'><textarea name='input_5' id='input_4_5' class='textarea small' placeholder='Comment' aria-invalid="false" rows='10' cols='50'></textarea></div></div></div></div>
<div class='gform_footer top_label'> <input type='submit' id='gform_submit_button_4' class='gform_button button' value='Submit' onclick='if(window["gf_submitting_4"]){return false;} if( !jQuery("#gform_4")[0].checkValidity || jQuery("#gform_4")[0].checkValidity()){window["gf_submitting_4"]=true;} ' onkeypress='if( event.keyCode == 13 ){ if(window["gf_submitting_4"]){return false;} if( !jQuery("#gform_4")[0].checkValidity || jQuery("#gform_4")[0].checkValidity()){window["gf_submitting_4"]=true;} jQuery("#gform_4").trigger("submit",[true]); }' />
<input type='hidden' class='gform_hidden' name='is_submit_4' value='1' />
<input type='hidden' class='gform_hidden' name='gform_submit' value='4' />
<input type='hidden' class='gform_hidden' name='gform_unique_id' value='' />
<input type='hidden' class='gform_hidden' name='state_4' value='WyJbXSIsImYwZjIwZGY4YmJlNjRmNTFjOTI1MjFhMWZiYmRiYzc4Il0=' />
<input type='hidden' class='gform_hidden' name='gform_target_page_number_4' id='gform_target_page_number_4' value='0' />
<input type='hidden' class='gform_hidden' name='gform_source_page_number_4' id='gform_source_page_number_4' value='1' />
<input type='hidden' name='gform_field_values' value='' />
</div>
</form>
</div><script type="text/javascript">
/* <![CDATA[ */
gform.initializeOnLoaded( function() {gformInitSpinner( 4, 'https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/images/spinner.svg', true );jQuery('#gform_ajax_frame_4').on('load',function(){var contents = jQuery(this).contents().find('*').html();var is_postback = contents.indexOf('GF_AJAX_POSTBACK') >= 0;if(!is_postback){return;}var form_content = jQuery(this).contents().find('#gform_wrapper_4');var is_confirmation = jQuery(this).contents().find('#gform_confirmation_wrapper_4').length > 0;var is_redirect = contents.indexOf('gformRedirect(){') >= 0;var is_form = form_content.length > 0 && ! is_redirect && ! is_confirmation;var mt = parseInt(jQuery('html').css('margin-top'), 10) + parseInt(jQuery('body').css('margin-top'), 10) + 100;if(is_form){jQuery('#gform_wrapper_4').html(form_content.html());if(form_content.hasClass('gform_validation_error')){jQuery('#gform_wrapper_4').addClass('gform_validation_error');} else {jQuery('#gform_wrapper_4').removeClass('gform_validation_error');}setTimeout( function() { /* delay the scroll by 50 milliseconds to fix a bug in chrome */ }, 50 );if(window['gformInitDatepicker']) {gformInitDatepicker();}if(window['gformInitPriceFields']) {gformInitPriceFields();}var current_page = jQuery('#gform_source_page_number_4').val();gformInitSpinner( 4, 'https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/images/spinner.svg', true );jQuery(document).trigger('gform_page_loaded', [4, current_page]);window['gf_submitting_4'] = false;}else if(!is_redirect){var confirmation_content = jQuery(this).contents().find('.GF_AJAX_POSTBACK').html();if(!confirmation_content){confirmation_content = contents;}jQuery('#gform_wrapper_4').replaceWith(confirmation_content);jQuery(document).trigger('gform_confirmation_loaded', [4]);window['gf_submitting_4'] = false;wp.a11y.speak(jQuery('#gform_confirmation_message_4').text());}else{jQuery('#gform_4').append(contents);if(window['gformRedirect']) {gformRedirect();}}jQuery(document).trigger("gform_pre_post_render", [{ formId: "4", currentPage: "current_page", abort: function() { this.preventDefault(); } }]); if (event && event.defaultPrevented) { return; } const gformWrapperDiv = document.getElementById( "gform_wrapper_4" ); if ( gformWrapperDiv ) { const visibilitySpan = document.createElement( "span" ); visibilitySpan.id = "gform_visibility_test_4"; gformWrapperDiv.insertAdjacentElement( "afterend", visibilitySpan ); } const visibilityTestDiv = document.getElementById( "gform_visibility_test_4" ); let postRenderFired = false; function triggerPostRender() { if ( postRenderFired ) { return; } postRenderFired = true; jQuery( document ).trigger( 'gform_post_render', [4, current_page] ); gform.utils.trigger( { event: 'gform/postRender', native: false, data: { formId: 4, currentPage: current_page } } ); if ( visibilityTestDiv ) { visibilityTestDiv.parentNode.removeChild( visibilityTestDiv ); } } function debounce( func, wait, immediate ) { var timeout; return function() { var context = this, args = arguments; var later = function() { timeout = null; if ( !immediate ) func.apply( context, args ); }; var callNow = immediate && !timeout; clearTimeout( timeout ); timeout = setTimeout( later, wait ); if ( callNow ) func.apply( context, args ); }; } const debouncedTriggerPostRender = debounce( function() { triggerPostRender(); }, 200 ); if ( visibilityTestDiv && visibilityTestDiv.offsetParent === null ) { const observer = new MutationObserver( ( mutations ) => { mutations.forEach( ( mutation ) => { if ( mutation.type === 'attributes' && visibilityTestDiv.offsetParent !== null ) { debouncedTriggerPostRender(); observer.disconnect(); } }); }); observer.observe( document.body, { attributes: true, childList: false, subtree: true, attributeFilter: [ 'style', 'class' ], }); } else { triggerPostRender(); } } );} );
/* ]]> */
</script>
<h6><strong>For reliable and quality <a href="https://precisebusinesssolutions.net/managed-it-services/">Managed IT Services,</a> <a href="https://precisebusinesssolutions.net/it-support/"> IT Support</a> and <a href="https://precisebusinesssolutions.net/pbx-systems/">VoIP,</a> </strong><strong>Contact <a href="https://precisebusinesssolutions.net/">Precise Business Solutions</a> </strong></h6>
<div id="comments" class="comments-area">
<div id="respond" class="comment-respond">
<h3 id="reply-title" class="comment-reply-title">Leave a Reply <small><a rel="nofollow" id="cancel-comment-reply-link" href="/2020/08/03/learn-seo-the-ultimate-guide-for-seo-beginners-2020/#respond" style="display:none;">Cancel reply</a></small></h3><form action="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-comments-post.php" method="post" id="commentform" class="comment-form"><p class="comment-notes text-small">Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked <span class="required">*</span></p><p class="comment-form-comment"><label class="assistive-text" for="comment">Comment</label><textarea id="comment" placeholder="Comment" name="comment" cols="45" rows="8" aria-required="true"></textarea></p><div class="form-fields"><span class="comment-form-author"><label class="assistive-text" for="author">Name *</label><input id="author" name="author" type="text" placeholder="Name*" value="" size="30" aria-required="true" /></span>
<span class="comment-form-email"><label class="assistive-text" for="email">Email *</label><input id="email" name="email" type="text" placeholder="Email*" value="" size="30" aria-required="true" /></span>
<span class="comment-form-url"><label class="assistive-text" for="url">Website</label><input id="url" name="url" type="text" placeholder="Website" value="" size="30" /></span></div>
<p class="comment-form-cookies-consent"><input id="wp-comment-cookies-consent" name="wp-comment-cookies-consent" type="checkbox" value="yes" /><label for="wp-comment-cookies-consent">Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.</label></p>
<p class="form-submit"><input name="submit" type="submit" id="submit" class="submit" value="Post Comment" /> <a href="javascript:void(0);" class="dt-btn dt-btn-m"><span>Post comment</span></a><input type='hidden' name='comment_post_ID' value='4210' id='comment_post_ID' />
<input type='hidden' name='comment_parent' id='comment_parent' value='0' />
</p></form> </div><!-- #respond -->
</div><!-- #comments .comments-area -->
</div><!-- #content -->
</div><!-- .wf-container -->
</div><!-- .wf-wrap -->
</div><!-- #main -->
<!-- !Footer -->
<footer id="footer" class="footer solid-bg">
<div class="wf-wrap">
<div class="wf-container-footer">
<div class="wf-container">
<section id="text-2" class="widget widget_text wf-cell wf-1-3"> <div class="textwidget"><p><a href="/digital-agency/wp-content/uploads/sites/46/2018/02/artfooter-agency.jpg"><img decoding="async" style="margin: 5px 0px 5px 0px; max-width: 200px;" src="/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Logo.png" /></a><br />
At Precise, we understand how tough and time consuming it can be to reach your target customer. We are here to utilize our vast experience and help gain exposure to your business.</p>
</div>
</section><section id="presscore-contact-info-widget-2" class="widget widget_presscore-contact-info-widget wf-cell wf-1-3"><div class="widget-title">Contact Info</div><ul class="contact-info"><li><span class="color-primary">Phone number</span><br />(281) 612-1133</li><li><span class="color-primary">Address</span><br />504 Spring Hill Dr. Suite 420<br>
Spring, TX 77386</li><li><span class="color-primary">Business Hours</span><br />24/7/365</li></ul><div class="soc-ico"><p class="assistive-text">Find us on:</p><a title="Facebook page opens in new window" href="#" target="_blank" class="facebook"><span class="soc-font-icon"></span><span class="screen-reader-text">Facebook page opens in new window</span></a><a title="Twitter page opens in new window" href="#" target="_blank" class="twitter"><span class="soc-font-icon"></span><span class="screen-reader-text">Twitter page opens in new window</span></a><a title="YouTube page opens in new window" href="#" target="_blank" class="you-tube"><span class="soc-font-icon"></span><span class="screen-reader-text">YouTube page opens in new window</span></a><a title="Linkedin page opens in new window" href="#" target="_blank" class="linkedin"><span class="soc-font-icon"></span><span class="screen-reader-text">Linkedin page opens in new window</span></a></div></section><section id="presscore-progress-bars-widget-3" class="widget widget_presscore-progress-bars-widget wf-cell wf-1-3"><div class="widget-title">Experience</div><div class="widget-info">Precise has 30+ years of combined experience in Web Design and Digital Marketing. But we don’t stop there, we understand that markets change and we have to evolve as marketing geniuses. </div><div class="skills animate-element"><div class="skill-name">Graphic and Video Design - 12 years</div><div class="skill"><div class="skill-value" data-width="100"></div></div><div class="skill-name">Web Design - 10 years</div><div class="skill"><div class="skill-value" data-width="80"></div></div><div class="skill-name">SEO - 8 years</div><div class="skill"><div class="skill-value" data-width="70"></div></div><div class="skill-name">Branding - 6 years</div><div class="skill"><div class="skill-value" data-width="50"></div></div></div></section><section id="presscore-blog-posts-3" class="widget widget_presscore-blog-posts wf-cell wf-1-3"><div class="widget-title">Recent Posts</div><ul class="recent-posts round-images"><li><article class="post-format-standard"><div class="mini-post-img"><a class="alignleft post-rollover no-avatar" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/25/etsy-com/" style="width:70px; height: 70px;" aria-label="Post image"></a></div><div class="post-content"><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/25/etsy-com/">etsy.com</a><br /><time datetime="2023-10-25T15:35:59+00:00">October 25, 2023</time></div></article></li><li><article class="post-format-standard"><div class="mini-post-img"><a class="alignleft post-rollover no-avatar" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/25/8721/" style="width:70px; height: 70px;" aria-label="Post image"></a></div><div class="post-content"><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/25/8721/">No title</a><br /><time datetime="2023-10-25T09:25:22+00:00">October 25, 2023</time></div></article></li><li><article class="post-format-standard"><div class="mini-post-img"><a class="alignleft post-rollover no-avatar" href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/24/8719/" style="width:70px; height: 70px;" aria-label="Post image"></a></div><div class="post-content"><a href="https://lightsforchristmas.co/2023/10/24/8719/">No title</a><br /><time datetime="2023-10-24T06:47:51+00:00">October 24, 2023</time></div></article></li></ul></section> </div><!-- .wf-container -->
</div><!-- .wf-container-footer -->
</div><!-- .wf-wrap -->
<div data-elementor-type="wp-post" data-elementor-id="4900" class="elementor elementor-4900" data-elementor-post-type="elementor-hf">
<section class="elementor-section elementor-top-section elementor-element elementor-element-27d32b2 elementor-section-content-middle elementor-section-boxed elementor-section-height-default elementor-section-height-default" data-id="27d32b2" data-element_type="section">
<div class="elementor-container elementor-column-gap-default">
<div class="elementor-column elementor-col-33 elementor-top-column elementor-element elementor-element-bd8b7fd" data-id="bd8b7fd" data-element_type="column">
<div class="elementor-widget-wrap elementor-element-populated">
<div class="elementor-element elementor-element-c5053db elementor-widget elementor-widget-image" data-id="c5053db" data-element_type="widget" data-widget_type="image.default">
<div class="elementor-widget-container">
<img src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/MR-LIGHTS-colorful.png" title="MR-LIGHTS colorful" alt="MR-LIGHTS colorful" loading="lazy" /> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="elementor-column elementor-col-33 elementor-top-column elementor-element elementor-element-a6c7887" data-id="a6c7887" data-element_type="column">
<div class="elementor-widget-wrap">
</div>
</div>
<div class="elementor-column elementor-col-33 elementor-top-column elementor-element elementor-element-5acdd7e" data-id="5acdd7e" data-element_type="column">
<div class="elementor-widget-wrap elementor-element-populated">
<div class="elementor-element elementor-element-c866286 elementor-icon-list--layout-traditional elementor-list-item-link-full_width elementor-widget elementor-widget-icon-list" data-id="c866286" data-element_type="widget" data-widget_type="icon-list.default">
<div class="elementor-widget-container">
<ul class="elementor-icon-list-items">
<li class="elementor-icon-list-item">
<span class="elementor-icon-list-icon">
<i aria-hidden="true" class="fas fa-map-marker-alt"></i> </span>
<span class="elementor-icon-list-text">21811 Leigh Creek Dr. Spring, TX 77388</span>
</li>
<li class="elementor-icon-list-item">
<span class="elementor-icon-list-icon">
<i aria-hidden="true" class="far fa-envelope-open"></i> </span>
<span class="elementor-icon-list-text">info@lightsforchristmas.co</span>
</li>
<li class="elementor-icon-list-item">
<a href="tel:(281)%20699-0025">
<span class="elementor-icon-list-icon">
<i aria-hidden="true" class="fas fa-phone-alt"></i> </span>
<span class="elementor-icon-list-text">(281) 699-0025</span>
</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</section>
<section class="elementor-section elementor-top-section elementor-element elementor-element-b6144ce elementor-section-content-middle elementor-section-boxed elementor-section-height-default elementor-section-height-default" data-id="b6144ce" data-element_type="section" data-settings="{"background_background":"classic"}">
<div class="elementor-container elementor-column-gap-default">
<div class="elementor-column elementor-col-50 elementor-top-column elementor-element elementor-element-eaa316c" data-id="eaa316c" data-element_type="column">
<div class="elementor-widget-wrap elementor-element-populated">
<div class="elementor-element elementor-element-35ab20a elementor-widget elementor-widget-text-editor" data-id="35ab20a" data-element_type="widget" data-widget_type="text-editor.default">
<div class="elementor-widget-container">
<div class="wf-float-left">MR LIGHTS 2021. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.</div> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="elementor-column elementor-col-50 elementor-top-column elementor-element elementor-element-c1331d5" data-id="c1331d5" data-element_type="column">
<div class="elementor-widget-wrap elementor-element-populated">
<div class="elementor-element elementor-element-f76764f elementor-widget elementor-widget-text-editor" data-id="f76764f" data-element_type="widget" data-widget_type="text-editor.default">
<div class="elementor-widget-container">
<p>Web Design Houston, Digital Marketing Houston by <a style="color: #ffffff;" href="https://precisebusinesssolutions.net"> <img style="width: 100px; margin-left: 3px; vertical-align: middle;" src="https://precisebusiness.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Precise-Business-Solutions-Logo-30.png" /> </a></p> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</section>
</div>
<!-- !Bottom-bar -->
<div id="bottom-bar" class="solid-bg logo-left" role="contentinfo">
<div class="wf-wrap">
<div class="wf-container-bottom">
<div class="wf-float-left">
MR LIGHTS 2021. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
</div>
<div class="wf-float-right">
<div class="mini-nav"><ul id="bottom-menu" role="menubar"><li class="menu-item menu-item-type-post_type menu-item-object-page menu-item-home menu-item-1642 first" role="presentation"><a href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/' data-level='1' role="menuitem"><span class="menu-item-text"><span class="menu-text">Home</span></span></a></li> </ul><div class="menu-select"><span class="customSelect1"><span class="customSelectInner">NAVIGATION</span></span></div></div><div class="bottom-text-block"><p>Web Design Houston, Digital Marketing Houston by <a style="color: #ffffff;" href="https://precisebusinesssolutions.net"> <img style="width: 100px; margin-left: 3px; vertical-align: middle;" src="https://precisebusiness.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Precise-Business-Solutions-Logo-30.png"> </a></p>
</div>
</div>
</div><!-- .wf-container-bottom -->
</div><!-- .wf-wrap -->
</div><!-- #bottom-bar -->
</footer><!-- #footer -->
<a href="#" class="scroll-top"><span class="screen-reader-text">Go to Top</span></a>
</div><!-- #page -->
<!-- Meta Pixel Event Code -->
<script type='text/javascript'>
document.addEventListener( 'wpcf7mailsent', function( event ) {
if( "fb_pxl_code" in event.detail.apiResponse){
eval(event.detail.apiResponse.fb_pxl_code);
}
}, false );
</script>
<!-- End Meta Pixel Event Code -->
<div id='fb-pxl-ajax-code'></div> <script type='text/javascript'>
const lazyloadRunObserver = () => {
const lazyloadBackgrounds = document.querySelectorAll( `.e-con.e-parent:not(.e-lazyloaded)` );
const lazyloadBackgroundObserver = new IntersectionObserver( ( entries ) => {
entries.forEach( ( entry ) => {
if ( entry.isIntersecting ) {
let lazyloadBackground = entry.target;
if( lazyloadBackground ) {
lazyloadBackground.classList.add( 'e-lazyloaded' );
}
lazyloadBackgroundObserver.unobserve( entry.target );
}
});
}, { rootMargin: '200px 0px 200px 0px' } );
lazyloadBackgrounds.forEach( ( lazyloadBackground ) => {
lazyloadBackgroundObserver.observe( lazyloadBackground );
} );
};
const events = [
'DOMContentLoaded',
'elementor/lazyload/observe',
];
events.forEach( ( event ) => {
document.addEventListener( event, lazyloadRunObserver );
} );
</script>
<link rel='stylesheet' id='gform_basic-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/assets/css/dist/basic.min.css?ver=2.8.18' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='gform_theme_components-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/assets/css/dist/theme-components.min.css?ver=2.8.18' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='gform_theme_ie11-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/assets/css/dist/theme-ie11.min.css?ver=2.8.18' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='gform_theme-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/assets/css/dist/theme.min.css?ver=2.8.18' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='elementor-post-4900-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/uploads/elementor/css/post-4900.css?ver=1726896139' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='widget-image-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor/assets/css/widget-image.min.css?ver=3.24.3' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='widget-icon-list-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor/assets/css/widget-icon-list.min.css?ver=3.24.3' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='widget-text-editor-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor/assets/css/widget-text-editor.min.css?ver=3.24.3' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='elementor-icons-shared-0-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor/assets/lib/font-awesome/css/fontawesome.min.css?ver=5.15.3' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='elementor-icons-fa-solid-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor/assets/lib/font-awesome/css/solid.min.css?ver=5.15.3' type='text/css' media='all' />
<link rel='stylesheet' id='elementor-icons-fa-regular-css' href='https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor/assets/lib/font-awesome/css/regular.min.css?ver=5.15.3' type='text/css' media='all' />
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/themes/dt-the7/js/main.min.js?ver=9.13.0.1" id="dt-main-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/honeypot/includes/js/wpa.js?ver=2.2.02" id="wpascript-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" id="wpascript-js-after">
/* <![CDATA[ */
wpa_field_info = {"wpa_field_name":"wsrezl2034","wpa_field_value":774288,"wpa_add_test":"no"}
/* ]]> */
</script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-includes/js/comment-reply.min.js?ver=6.7.2" id="comment-reply-js" async="async" data-wp-strategy="async"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/themes/dt-the7/lib/jquery-mousewheel/jquery-mousewheel.min.js?ver=9.13.0.1" id="jquery-mousewheel-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/themes/dt-the7/lib/custom-scrollbar/custom-scrollbar.min.js?ver=9.13.0.1" id="the7-custom-scrollbar-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-includes/js/dist/dom-ready.min.js?ver=f77871ff7694fffea381" id="wp-dom-ready-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-includes/js/dist/hooks.min.js?ver=4d63a3d491d11ffd8ac6" id="wp-hooks-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-includes/js/dist/i18n.min.js?ver=5e580eb46a90c2b997e6" id="wp-i18n-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" id="wp-i18n-js-after">
/* <![CDATA[ */
wp.i18n.setLocaleData( { 'text direction\u0004ltr': [ 'ltr' ] } );
/* ]]> */
</script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-includes/js/dist/a11y.min.js?ver=3156534cc54473497e14" id="wp-a11y-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" defer='defer' src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/js/jquery.json.min.js?ver=2.8.18" id="gform_json-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" id="gform_gravityforms-js-extra">
/* <![CDATA[ */
var gform_i18n = {"datepicker":{"days":{"monday":"Mo","tuesday":"Tu","wednesday":"We","thursday":"Th","friday":"Fr","saturday":"Sa","sunday":"Su"},"months":{"january":"January","february":"February","march":"March","april":"April","may":"May","june":"June","july":"July","august":"August","september":"September","october":"October","november":"November","december":"December"},"firstDay":1,"iconText":"Select date"}};
var gf_legacy_multi = [];
var gform_gravityforms = {"strings":{"invalid_file_extension":"This type of file is not allowed. Must be one of the following:","delete_file":"Delete this file","in_progress":"in progress","file_exceeds_limit":"File exceeds size limit","illegal_extension":"This type of file is not allowed.","max_reached":"Maximum number of files reached","unknown_error":"There was a problem while saving the file on the server","currently_uploading":"Please wait for the uploading to complete","cancel":"Cancel","cancel_upload":"Cancel this upload","cancelled":"Cancelled"},"vars":{"images_url":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-content\/plugins\/gravityforms\/images"}};
var gf_global = {"gf_currency_config":{"name":"U.S. Dollar","symbol_left":"$","symbol_right":"","symbol_padding":"","thousand_separator":",","decimal_separator":".","decimals":2,"code":"USD"},"base_url":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-content\/plugins\/gravityforms","number_formats":[],"spinnerUrl":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-content\/plugins\/gravityforms\/images\/spinner.svg","version_hash":"8e45cae525d5ba84ae85e6aa43f10b8a","strings":{"newRowAdded":"New row added.","rowRemoved":"Row removed","formSaved":"The form has been saved. The content contains the link to return and complete the form."}};
var gf_global = {"gf_currency_config":{"name":"U.S. Dollar","symbol_left":"$","symbol_right":"","symbol_padding":"","thousand_separator":",","decimal_separator":".","decimals":2,"code":"USD"},"base_url":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-content\/plugins\/gravityforms","number_formats":[],"spinnerUrl":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-content\/plugins\/gravityforms\/images\/spinner.svg","version_hash":"8e45cae525d5ba84ae85e6aa43f10b8a","strings":{"newRowAdded":"New row added.","rowRemoved":"Row removed","formSaved":"The form has been saved. The content contains the link to return and complete the form."}};
/* ]]> */
</script>
<script type="text/javascript" defer='defer' src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/js/gravityforms.min.js?ver=2.8.18" id="gform_gravityforms-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" defer='defer' src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/js/jquery.maskedinput.min.js?ver=2.8.18" id="gform_masked_input-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" defer='defer' src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/js/placeholders.jquery.min.js?ver=2.8.18" id="gform_placeholder-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" defer='defer' src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/assets/js/dist/utils.min.js?ver=50c7bea9c2320e16728e44ae9fde5f26" id="gform_gravityforms_utils-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" defer='defer' src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/assets/js/dist/vendor-theme.min.js?ver=54e7080aa7a02c83aa61fae430b9d869" id="gform_gravityforms_theme_vendors-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" id="gform_gravityforms_theme-js-extra">
/* <![CDATA[ */
var gform_theme_config = {"common":{"form":{"honeypot":{"version_hash":"8e45cae525d5ba84ae85e6aa43f10b8a"}}},"hmr_dev":"","public_path":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-content\/plugins\/gravityforms\/assets\/js\/dist\/"};
/* ]]> */
</script>
<script type="text/javascript" defer='defer' src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/gravityforms/assets/js/dist/scripts-theme.min.js?ver=bab19fd84843dabc070e73326d787910" id="gform_gravityforms_theme-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor-pro/assets/js/webpack-pro.runtime.min.js?ver=3.24.2" id="elementor-pro-webpack-runtime-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor/assets/js/webpack.runtime.min.js?ver=3.24.3" id="elementor-webpack-runtime-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor/assets/js/frontend-modules.min.js?ver=3.24.3" id="elementor-frontend-modules-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" id="elementor-pro-frontend-js-before">
/* <![CDATA[ */
var ElementorProFrontendConfig = {"ajaxurl":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-admin\/admin-ajax.php","nonce":"fd30a363ab","urls":{"assets":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-content\/plugins\/elementor-pro\/assets\/","rest":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-json\/"},"settings":{"lazy_load_background_images":true},"shareButtonsNetworks":{"facebook":{"title":"Facebook","has_counter":true},"twitter":{"title":"Twitter"},"linkedin":{"title":"LinkedIn","has_counter":true},"pinterest":{"title":"Pinterest","has_counter":true},"reddit":{"title":"Reddit","has_counter":true},"vk":{"title":"VK","has_counter":true},"odnoklassniki":{"title":"OK","has_counter":true},"tumblr":{"title":"Tumblr"},"digg":{"title":"Digg"},"skype":{"title":"Skype"},"stumbleupon":{"title":"StumbleUpon","has_counter":true},"mix":{"title":"Mix"},"telegram":{"title":"Telegram"},"pocket":{"title":"Pocket","has_counter":true},"xing":{"title":"XING","has_counter":true},"whatsapp":{"title":"WhatsApp"},"email":{"title":"Email"},"print":{"title":"Print"},"x-twitter":{"title":"X"},"threads":{"title":"Threads"}},"facebook_sdk":{"lang":"en_US","app_id":""},"lottie":{"defaultAnimationUrl":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-content\/plugins\/elementor-pro\/modules\/lottie\/assets\/animations\/default.json"}};
/* ]]> */
</script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor-pro/assets/js/frontend.min.js?ver=3.24.2" id="elementor-pro-frontend-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-includes/js/jquery/ui/core.min.js?ver=1.13.3" id="jquery-ui-core-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" id="elementor-frontend-js-before">
/* <![CDATA[ */
var elementorFrontendConfig = {"environmentMode":{"edit":false,"wpPreview":false,"isScriptDebug":false},"i18n":{"shareOnFacebook":"Share on Facebook","shareOnTwitter":"Share on Twitter","pinIt":"Pin it","download":"Download","downloadImage":"Download image","fullscreen":"Fullscreen","zoom":"Zoom","share":"Share","playVideo":"Play Video","previous":"Previous","next":"Next","close":"Close","a11yCarouselWrapperAriaLabel":"Carousel | Horizontal scrolling: Arrow Left & Right","a11yCarouselPrevSlideMessage":"Previous slide","a11yCarouselNextSlideMessage":"Next slide","a11yCarouselFirstSlideMessage":"This is the first slide","a11yCarouselLastSlideMessage":"This is the last slide","a11yCarouselPaginationBulletMessage":"Go to slide"},"is_rtl":false,"breakpoints":{"xs":0,"sm":480,"md":768,"lg":1025,"xl":1440,"xxl":1600},"responsive":{"breakpoints":{"mobile":{"label":"Mobile Portrait","value":767,"default_value":767,"direction":"max","is_enabled":true},"mobile_extra":{"label":"Mobile Landscape","value":880,"default_value":880,"direction":"max","is_enabled":false},"tablet":{"label":"Tablet Portrait","value":1024,"default_value":1024,"direction":"max","is_enabled":true},"tablet_extra":{"label":"Tablet Landscape","value":1200,"default_value":1200,"direction":"max","is_enabled":false},"laptop":{"label":"Laptop","value":1366,"default_value":1366,"direction":"max","is_enabled":false},"widescreen":{"label":"Widescreen","value":2400,"default_value":2400,"direction":"min","is_enabled":false}}},"version":"3.24.3","is_static":false,"experimentalFeatures":{"additional_custom_breakpoints":true,"container_grid":true,"e_swiper_latest":true,"e_nested_atomic_repeaters":true,"e_onboarding":true,"theme_builder_v2":true,"home_screen":true,"ai-layout":true,"landing-pages":true,"link-in-bio":true,"floating-buttons":true,"display-conditions":true,"form-submissions":true},"urls":{"assets":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-content\/plugins\/elementor\/assets\/","ajaxurl":"https:\/\/lightsforchristmas.co\/wp-admin\/admin-ajax.php"},"nonces":{"floatingButtonsClickTracking":"a3e3c0d78a"},"swiperClass":"swiper","settings":{"page":[],"editorPreferences":[]},"kit":{"active_breakpoints":["viewport_mobile","viewport_tablet"],"global_image_lightbox":"yes","lightbox_enable_counter":"yes","lightbox_enable_fullscreen":"yes","lightbox_enable_zoom":"yes","lightbox_enable_share":"yes","lightbox_title_src":"title","lightbox_description_src":"description"},"post":{"id":4210,"title":"Learn%20SEO%3A%20The%20Ultimate%20Guide%20For%20SEO%20Beginners%20%5B2020%5D%20-%20Lights%20For%20Christmas","excerpt":"Chapter 1Before we dive into specific techniques and aspects of how to learn SEO in 2020, let\u2019s start with the basic stuff in the first chapter. Are you ready? Welcome to the ultimate SEO guide for beginners!Are you new to SEO? Do you wonder how it works and what matters most in 2020? You\u2019re at…","featuredImage":false}};
/* ]]> */
</script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor/assets/js/frontend.min.js?ver=3.24.3" id="elementor-frontend-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://lightsforchristmas.co/wp-content/plugins/elementor-pro/assets/js/elements-handlers.min.js?ver=3.24.2" id="pro-elements-handlers-js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
/* <![CDATA[ */
gform.initializeOnLoaded( function() { jQuery(document).on('gform_post_render', function(event, formId, currentPage){if(formId == 4) {if(typeof Placeholders != 'undefined'){
Placeholders.enable();
}jQuery('#input_4_3').mask('(999) 999-9999').bind('keypress', function(e){if(e.which == 13){jQuery(this).blur();} } );} } );jQuery(document).on('gform_post_conditional_logic', function(event, formId, fields, isInit){} ) } );
/* ]]> */
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
/* <![CDATA[ */
gform.initializeOnLoaded( function() {jQuery(document).trigger("gform_pre_post_render", [{ formId: "4", currentPage: "1", abort: function() { this.preventDefault(); } }]); if (event && event.defaultPrevented) { return; } const gformWrapperDiv = document.getElementById( "gform_wrapper_4" ); if ( gformWrapperDiv ) { const visibilitySpan = document.createElement( "span" ); visibilitySpan.id = "gform_visibility_test_4"; gformWrapperDiv.insertAdjacentElement( "afterend", visibilitySpan ); } const visibilityTestDiv = document.getElementById( "gform_visibility_test_4" ); let postRenderFired = false; function triggerPostRender() { if ( postRenderFired ) { return; } postRenderFired = true; jQuery( document ).trigger( 'gform_post_render', [4, 1] ); gform.utils.trigger( { event: 'gform/postRender', native: false, data: { formId: 4, currentPage: 1 } } ); if ( visibilityTestDiv ) { visibilityTestDiv.parentNode.removeChild( visibilityTestDiv ); } } function debounce( func, wait, immediate ) { var timeout; return function() { var context = this, args = arguments; var later = function() { timeout = null; if ( !immediate ) func.apply( context, args ); }; var callNow = immediate && !timeout; clearTimeout( timeout ); timeout = setTimeout( later, wait ); if ( callNow ) func.apply( context, args ); }; } const debouncedTriggerPostRender = debounce( function() { triggerPostRender(); }, 200 ); if ( visibilityTestDiv && visibilityTestDiv.offsetParent === null ) { const observer = new MutationObserver( ( mutations ) => { mutations.forEach( ( mutation ) => { if ( mutation.type === 'attributes' && visibilityTestDiv.offsetParent !== null ) { debouncedTriggerPostRender(); observer.disconnect(); } }); }); observer.observe( document.body, { attributes: true, childList: false, subtree: true, attributeFilter: [ 'style', 'class' ], }); } else { triggerPostRender(); } } );
/* ]]> */
</script>
<div class="pswp" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="pswp__bg"></div>
<div class="pswp__scroll-wrap">
<div class="pswp__container">
<div class="pswp__item"></div>
<div class="pswp__item"></div>
<div class="pswp__item"></div>
</div>
<div class="pswp__ui pswp__ui--hidden">
<div class="pswp__top-bar">
<div class="pswp__counter"></div>
<button class="pswp__button pswp__button--close" title="Close (Esc)" aria-label="Close (Esc)"></button>
<button class="pswp__button pswp__button--share" title="Share" aria-label="Share"></button>
<button class="pswp__button pswp__button--fs" title="Toggle fullscreen" aria-label="Toggle fullscreen"></button>
<button class="pswp__button pswp__button--zoom" title="Zoom in/out" aria-label="Zoom in/out"></button>
<div class="pswp__preloader">
<div class="pswp__preloader__icn">
<div class="pswp__preloader__cut">
<div class="pswp__preloader__donut"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="pswp__share-modal pswp__share-modal--hidden pswp__single-tap">
<div class="pswp__share-tooltip"></div>
</div>
<button class="pswp__button pswp__button--arrow--left" title="Previous (arrow left)" aria-label="Previous (arrow left)">
</button>
<button class="pswp__button pswp__button--arrow--right" title="Next (arrow right)" aria-label="Next (arrow right)">
</button>
<div class="pswp__caption">
<div class="pswp__caption__center"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>






























